Quick Links
Do you ever feel like navigating your Windows system is like a never-ending scavenger hunt?
You click through endless menus and folders, just trying to find that one file or setting.
That’s where these commands come in.
Hannah Stryker / How-To Geek
Its like having a secret shortcut to get things done faster.
All the commands listed in this article can be used in both Command Prompt and PowerShell.
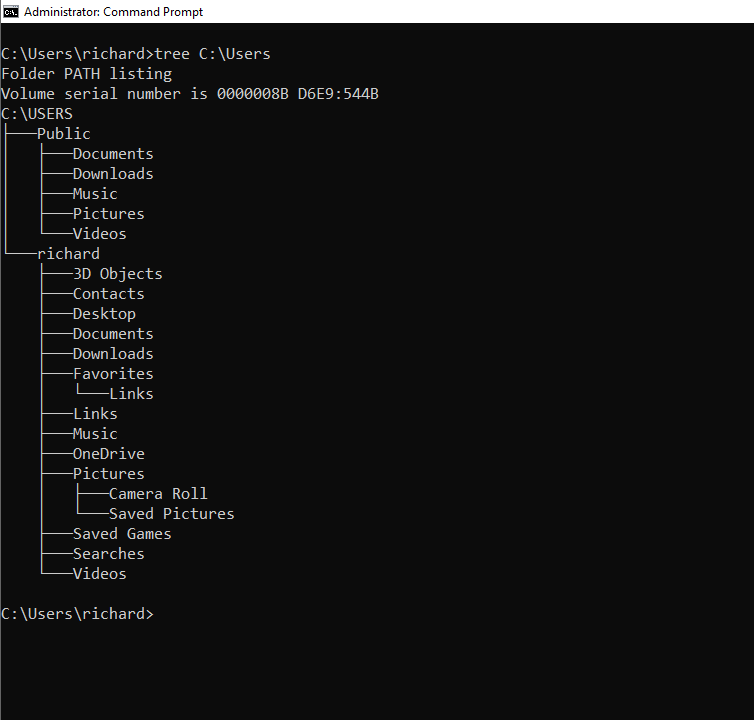
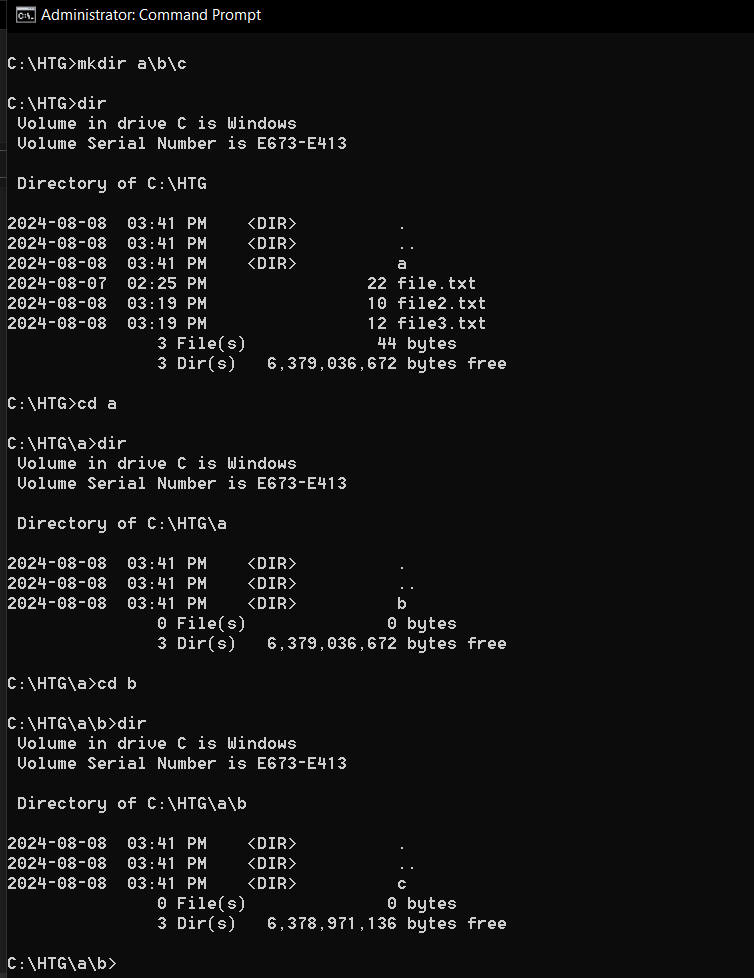
1cd: Change Directories Easily
Navigating the Windows file systemdoesn’t have to be a maze.
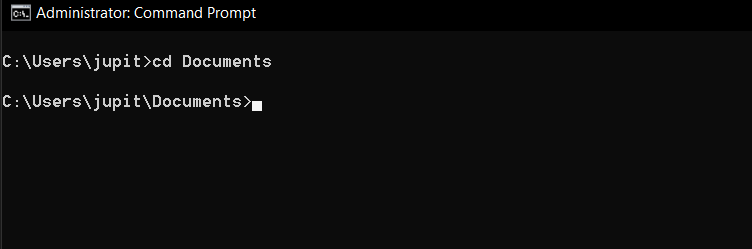
The cd (change directory) command makes it easy to move around your directories.
To use the command, just typecdfollowed by the directory you want to navigate to.
Need to quickly jump to your Documents folder from your home directory?
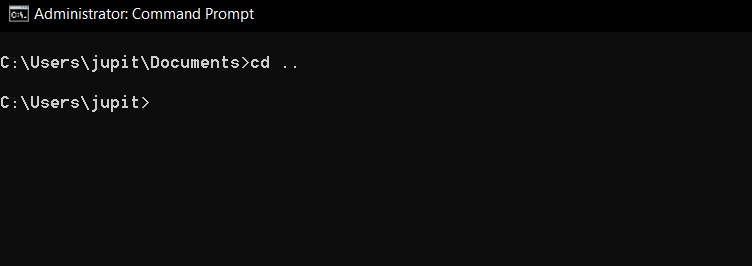
This can be useful if you oughta navigate through different directories quickly.
Remember to use the correct syntax and spelling.
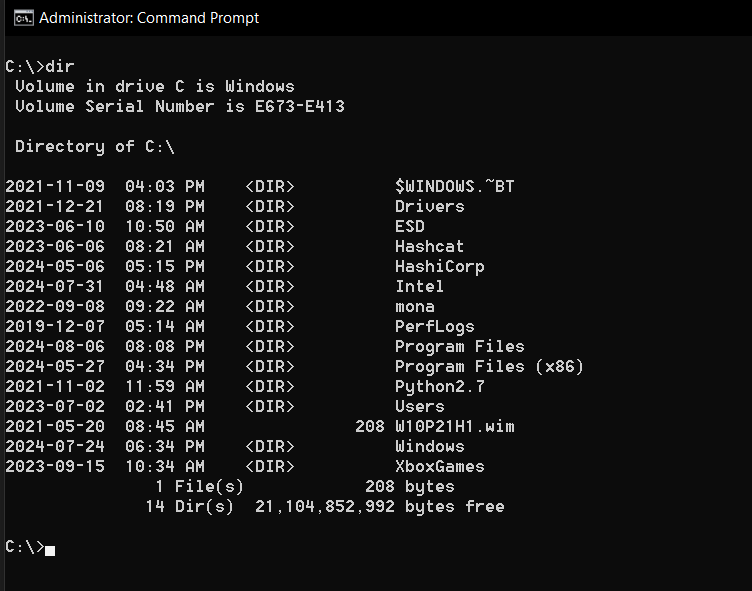
The dir (directory) command is your answer.
It lists all files and directories right in the terminal.
Just typedirto get a list of everything in the current directory.
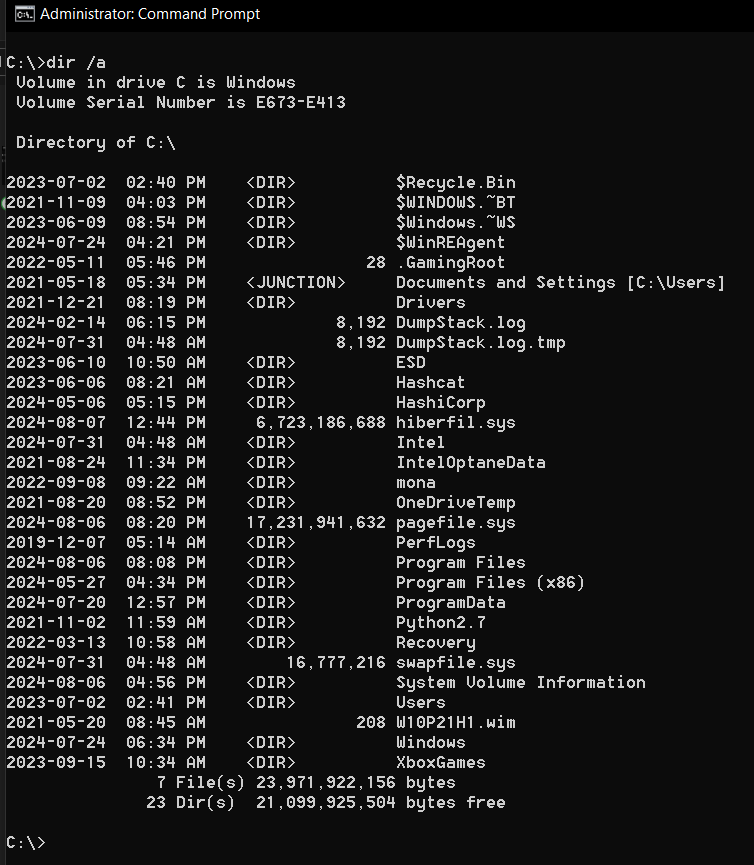
If you typedir /ayou can see all files and folders, including hidden ones, displayed in the directory.
Use the Tab key to auto-complete file and directory names while typing commands, saving time and reducing errors.
Create new folders wherever you want.
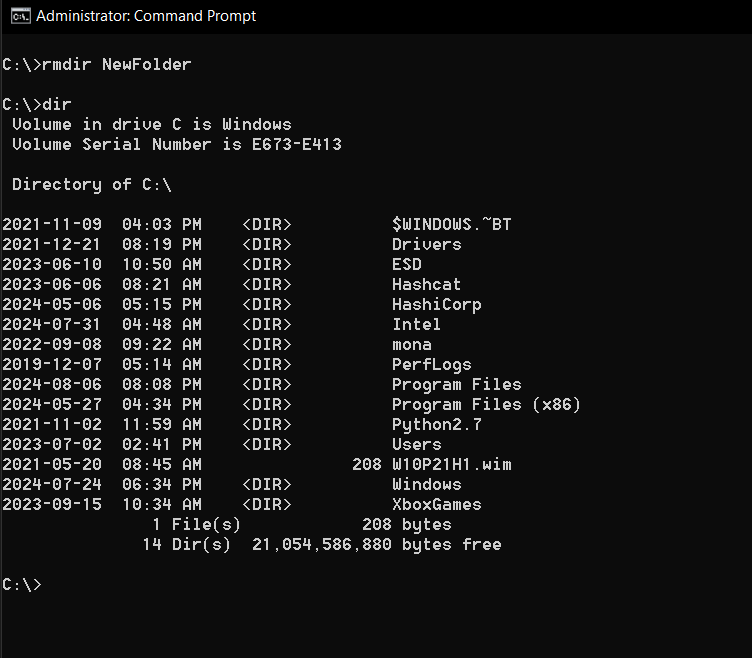
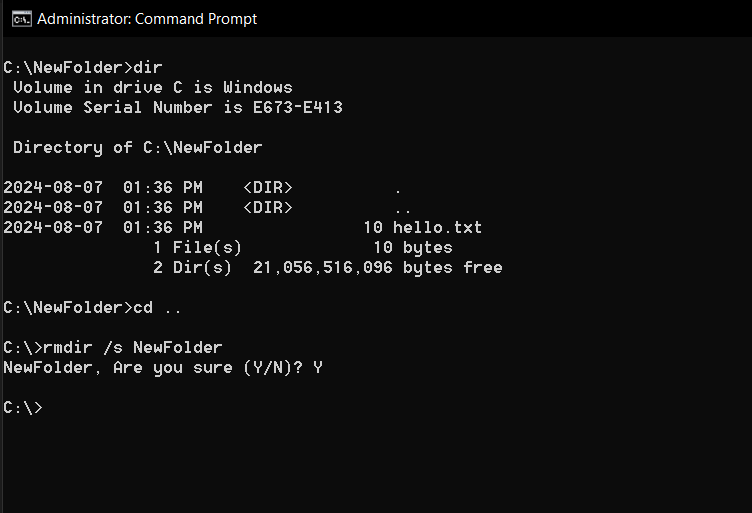
4rmdir: Remove Directories
Do you have an empty folder you dont need?
The rmdir (remove directory) command will take care of it.
But if its not empty, youll need a different approach.
Just be careful with that second one, and double-check you really want everything gone.
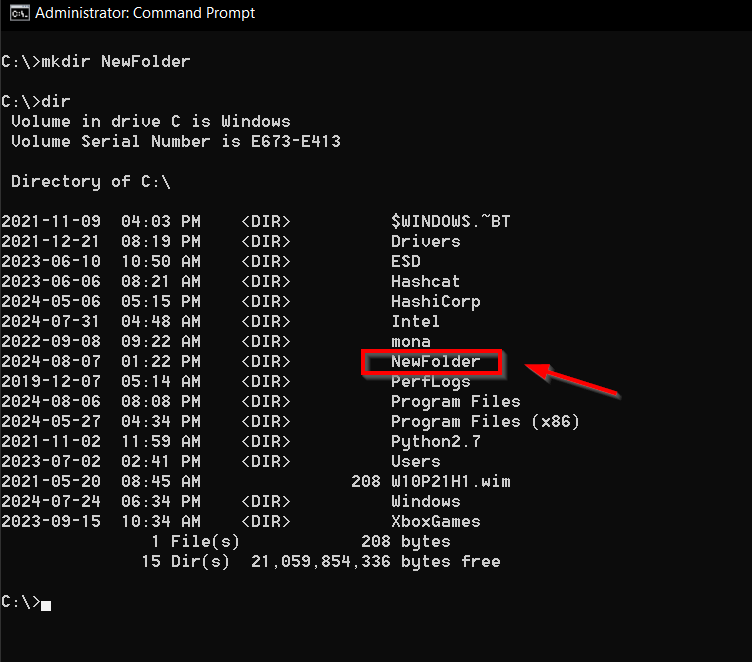
If the action is successful, the new directory will appear or disappear from the list accordingly.
If you need more information on a specific command, simply enter help followed by the command.
For example, if you need more information on the rmdir command, jot down thehelp rmdircommand.
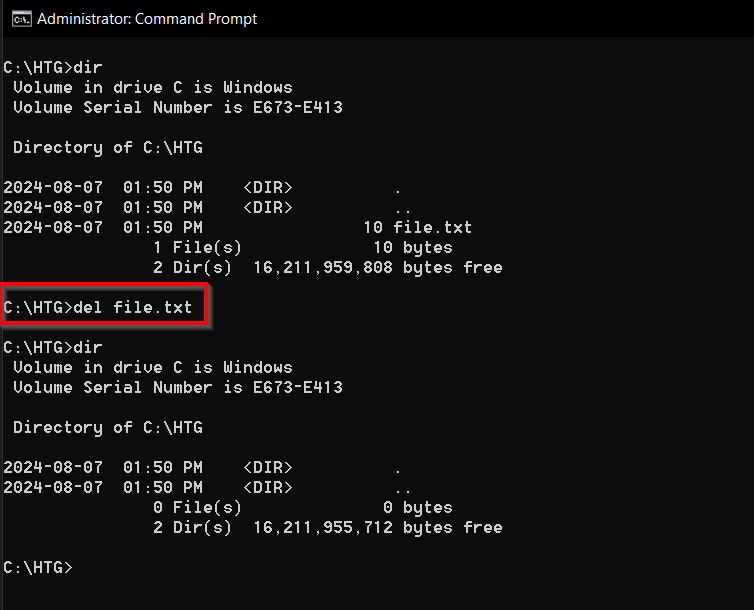
5del: Delete Files
Do you’re gonna wanna delete a file?
The del command will do it.
The del command doesn’t print anything in response to its use, which might surprise you.
Once you fire off the command, the file will be deleted silently.
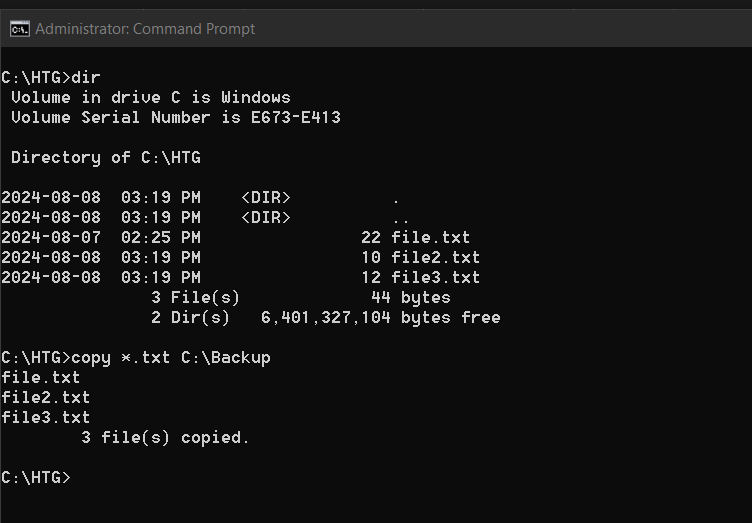
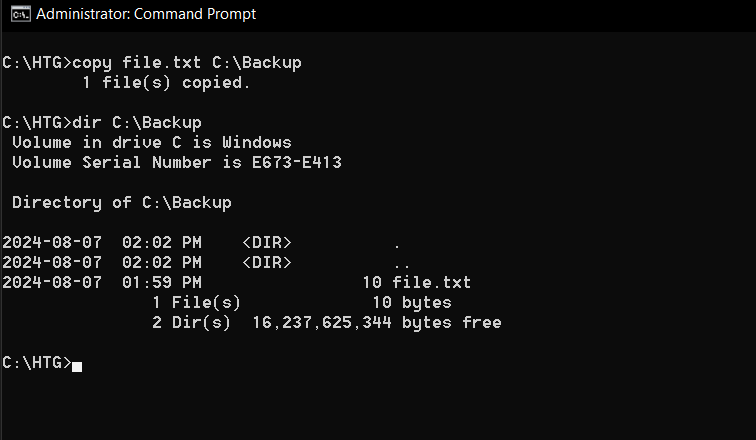
6copy: Copy Files to Another Location
Do you want to back up your files?
The copy command makes duplicating files a breeze.
This allows you to easily re-run previous commands without retyping them.
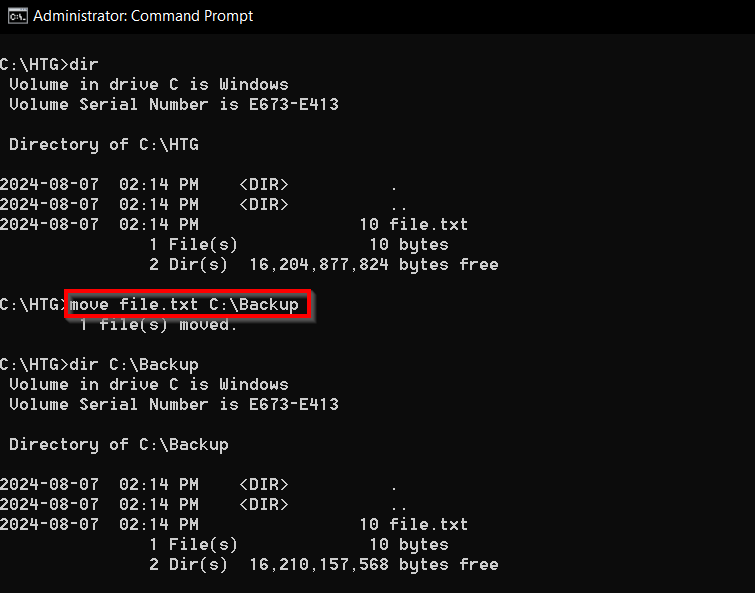
7move: Move Files to a New Location
Are you reorganizing your files?
The move command lets you move files around on Windows without having to copy them to a new location.
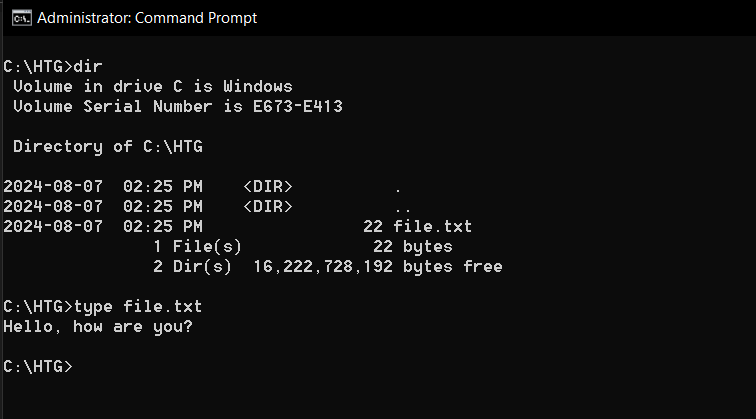
The bang out command displays its contents right in the terminal.
This can be done by entering key in followed by the text file you want to read.
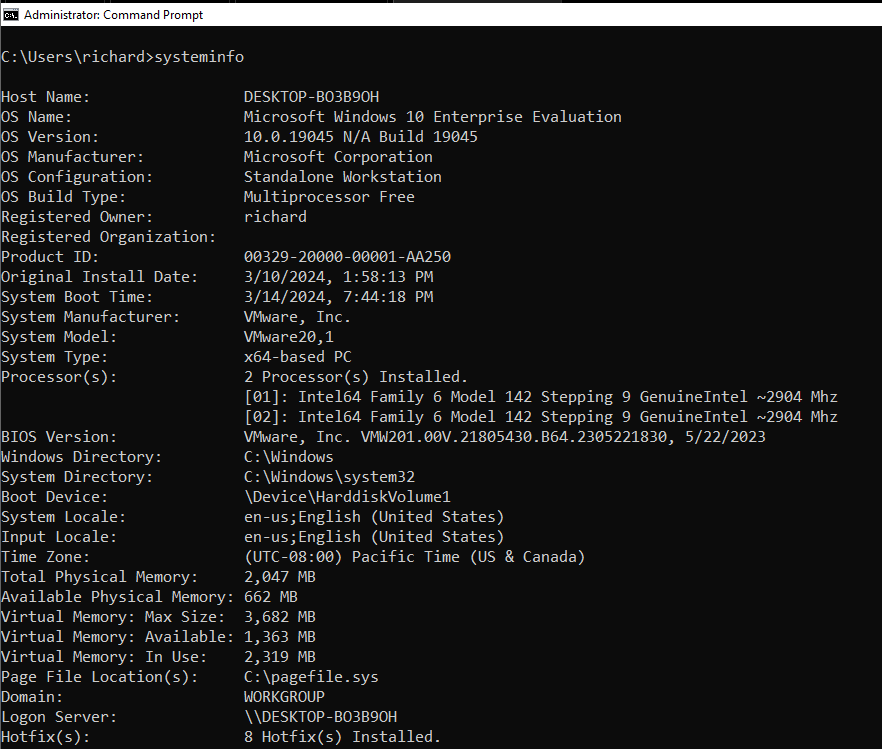
It displays information such as the operating system version, processor pop in, and installed RAM.
It also includes details about the computer’s web connection configuration.
It’s a handy way to see the layout of your files and folders.
Keep exploring, keep experimenting, and watch your command-line skills grow.