Quick Links
Microsoft Excel offershundreds of functions.
So, there’s bound to be at least a handful you don’t know exist.
These unique functions have specific purposes that you’ll be thrilled to learn about and use.
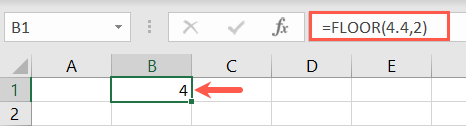
Use FLOOR to round down and CEILING to round up.
The syntax for each is
and
where both arguments are required.
Use MODE.SNGL to find a single frequently recurring number in an array or cell range.
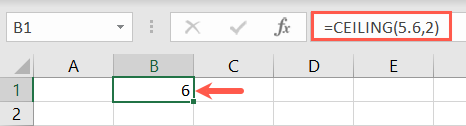
The syntax isMODE.SNGL(array1, array2, …)where only the first argument is required.
you might use numbers, names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
Use the optional argument(s) for additional cell ranges.
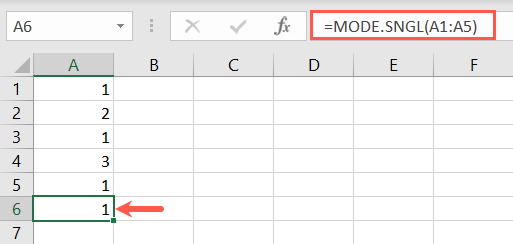
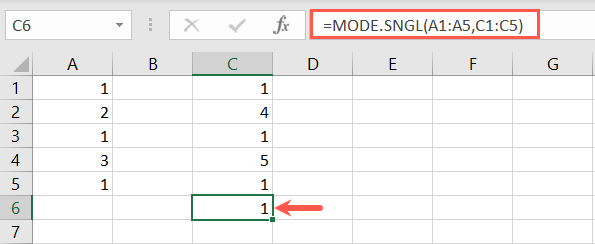
Here, we look for the repetitive number that appears the most in cells A1 through A5.
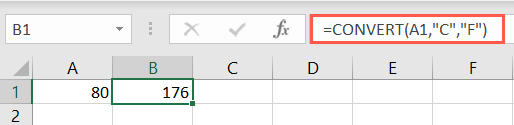
For thefromandtoarguments, you’ll use an abbreviation.
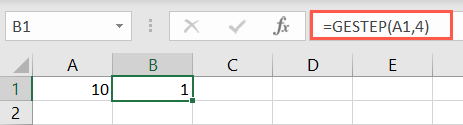
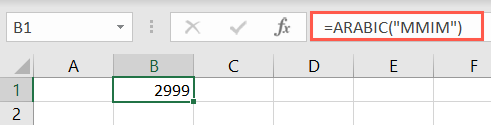
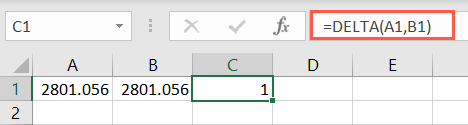
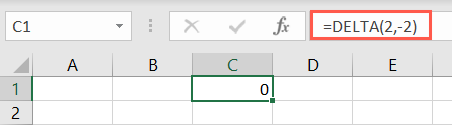
With it, you’ll use theKronecker deltafunction to test whether two values are equal.
Different than theEXACT function, the result is either 1 (true) or 0 (false).
If you leave the second argument blank, Excel assumes zero.
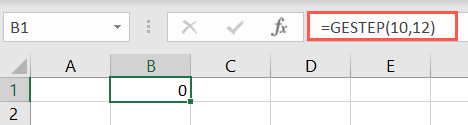
The result is either 1 (true) or 0 (false).
If you leave the second argument blank, Excel uses zero.
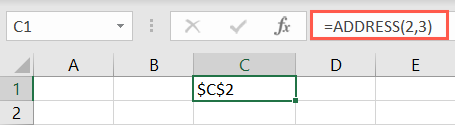
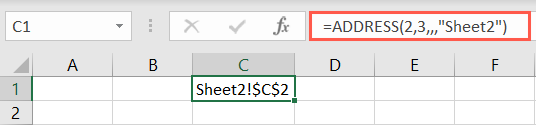
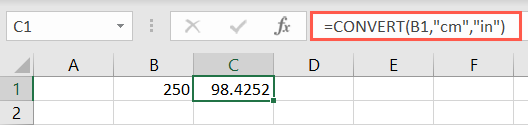
To find the exact address of a cell, you could use the ADDRESS function.
This is convenient if you want an error-freereference to a cell.
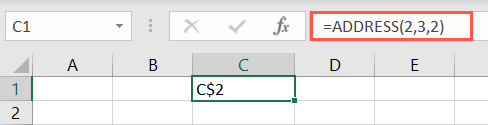
Enter the row number for the first argument and the column number for the second.
Note that the commas represent the blank argumentstypeandstyle.
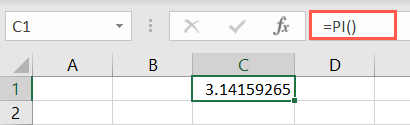
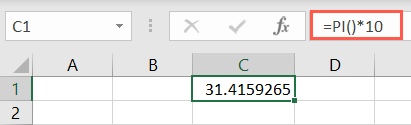
The syntax is simplyPI()with no arguments.
you’re able to add moreelements to the formulaif you want to use the value for a calculation.
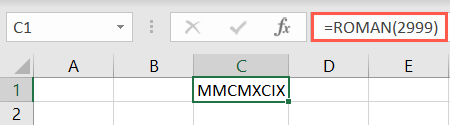
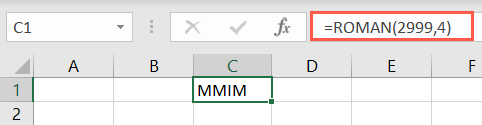
The optional argument for the ROMAN function specifies the pop in of Roman numeral from Classic to Simplified.
Enter the number 0, word TRUE, or omit the argument for Classic.
Use a 1, 2, or 3 for a more concise result.
Or, enter the number 4 or the word FALSE for Simplified.
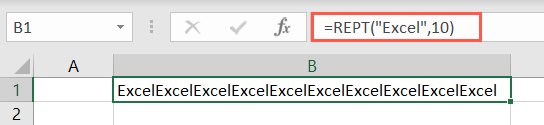
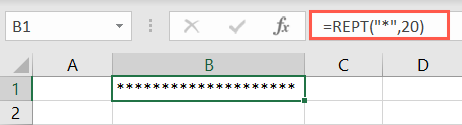
Enter the text argument within quotes and then the number of times to repeat that text.