You just plugged in yournew Wi-Fi router.
And trust us, we get it.
over the next day or two.

Jordan Gloor / How-To Geek
First, you better put yourISP’s combo unit into bridge mode.
Update the Administrator Password
The administrator password is a frequently overlooked aspect of router security.
Newer models might have pseudo-random passwords.
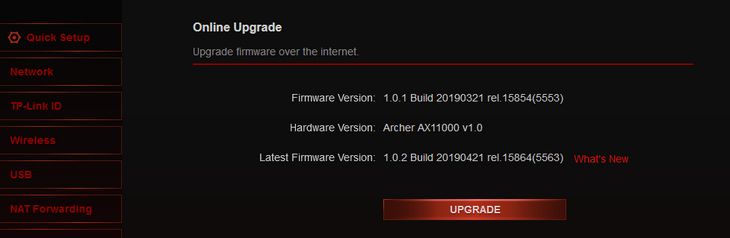
In both cases, the password is almost always printed directly on the label attached to the router.
Unlikeearlier Wi-Fi encryption standards that are now deprecated, WPA2 AES is still considered secure.
Change the Default Wi-Fi Password
Most routers now come with a pseudo-random password set as the default.
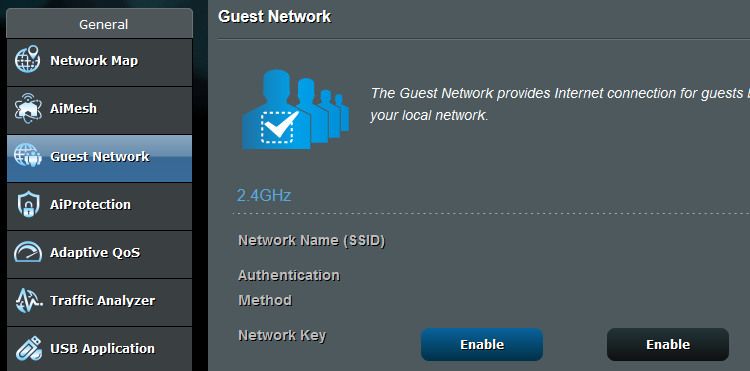
Like the admin login and password, that password is usually on a sticker attached to the router.
As always, avoid any identifying information.
Switching from a default SSID of “Netgear98” to “Apartment2A” is a security downgrade.
Why does it matter?
Check outthese Wi-Fi guest web connection best practiceswhen you set up your guest web connection.
They do, in fairness, do that.
But they also introduced a bunch of security vulnerabilities.
Some routers no longer include WPS, but you should check yours regardless and disable it.
you might be thinking.
Better yet, put a reminder on your calendar to revisit the topic.
How soon should you consider a replacement?
We recommend peoplereplace their Wi-Fi routers every 3-5 years.
If you want better performance and regular feature updates, upgrade every three years.
If you want to avoid obsolescence and security problems, upgrade every five.