Quick Links
Summary
6G is the sixth-generation cellular web connection currently under early development.
6G could potentially include additional cellular frequencies for dramatically faster speeds.
Expect it to arrive in the early 2030s.

Curious about 6G and when upgrading to 6G will even a possibility?
Here’s what we know.
What Is 6G?
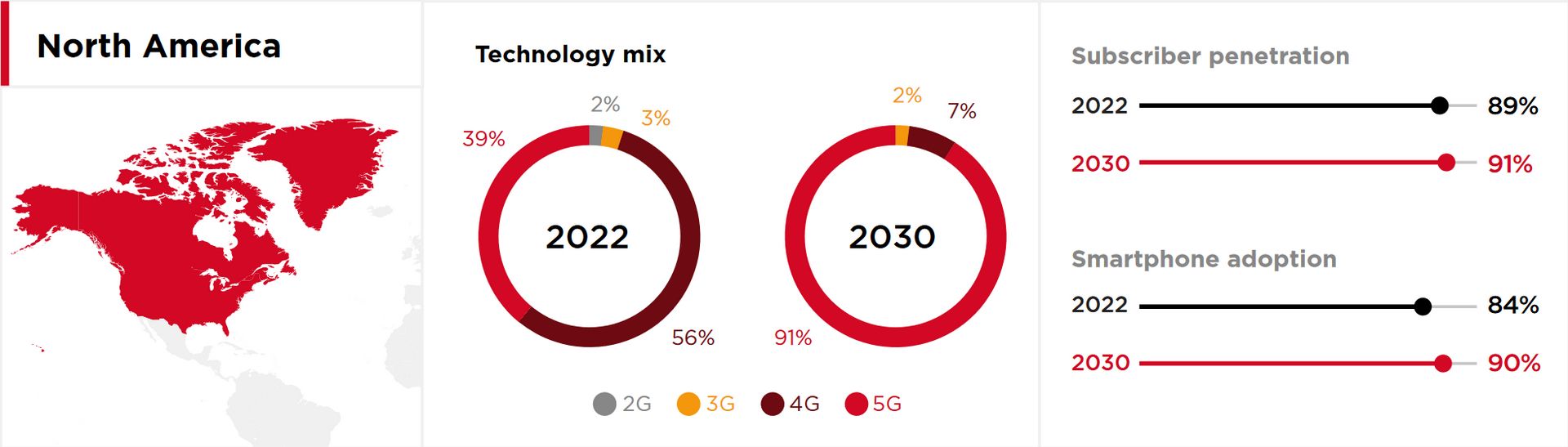
GMSA
“6G” is shorthand for sixth-generation cellular web link technology.
Roughly every ten years after that, a new generation of cellular tech arrived.
2G arrived in 1992, 3G in 2001, 4G in 2009, and5Gin 2019.
6G is the upcoming sixth-generation cellular connection technology that is currently in early development.
As of 2023, there are no established standards, let alone deployed 6G networks or devices.
That said, we do have some idea what 6G will look like.
Current cellular technology operates in the Megahertz (MHz) and the lower Gigahertz (GHz) frequency ranges.
The use of these frequencies will allow for data transmission well beyond the bandwidth capacity of current cellular technology.
How Fast Will 6G Be?
Those speeds are, respectively, 20 and 100 times higher than the theoretical peak 5G speeds.
Related:Comcast’s Xfinity 10G internet: What Exactly Is It?
When Will 6G Come Out?
6G web link development is active but still in its infancy.
It’ll be several more years before 6G is standardized.
Ericsson’s6G messagingechoes the early 2030s timeframe too, as do variousinterviews with telecom executives.
Given the current development timelines, you should expect a delivery arc similar to the 5G rollout.
After all, 5G was first introduced in 2019.
And even if they have 5G, they’re still often confused and disappointed bylackluster speeds and deceptive rollouts.