To get around this limitation, we can use the built-in gconf-editor utility to assign them ourselves.
First you’ll want to load up gconf-editor by typing it into the Alt+F2 Run dialog.
Once in the software, navigate to the following key.
If you are familiar with regedit on Windows, this is very similar.
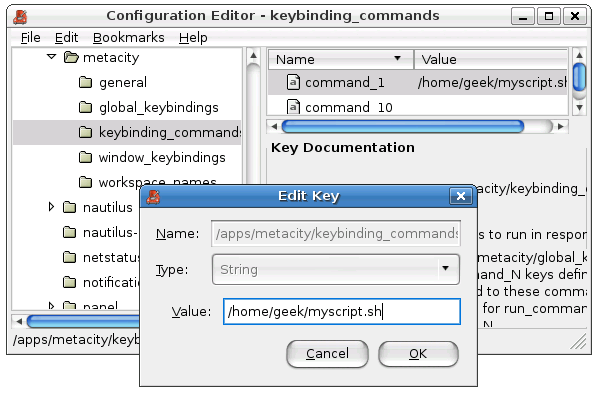
apps \ metacity \ keybinding_commands
You’ll notice a bunch of values on the right.
These are the available commands that you might create for assigning to shortcut keys in the next step.
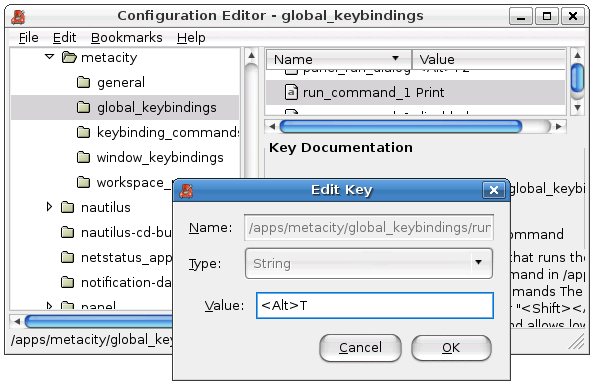
Here you will want to select run_command_1.
Enter in the shortcut key in plain text.
For instance, for Alt+T, you’ll do T.
you could also create custom commands in the keybinding_commands and assign them in the global_keybindings if you want.
Just remember that the keybindings will start with run_(name of command).