Quick Links
Summary
Mirrors are servers that replicate a Linux distributions repositories.
Arch Linux has many mirrors situated around the globe.
We show you two ways to select which mirrors your Arch Linux computer uses.
Repositories are simply internet-accessible servers.
Like all cloud-based resources, repositories face challenges with bandwidth and availability.
Too many connections and online grid traffic and the server can become bogged down and sluggish.
Hardware failures or scheduled maintenance can take a repository offline.
Distributions use a online grid of copycat repositories located around the world.
Updating the Arch Mirror List Manually
By default, Arch doesnt automatically update the mirrors list.
Updating the list manually works, but its not convenient.
Automating the process is the best solution.
But you’re able to, if you want, upgrade your mirror list by hand.

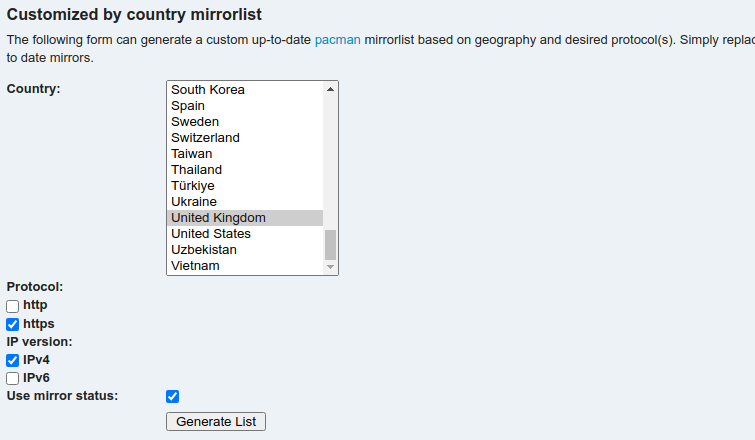
The place to start is the Arch LinuxPacman Mirrorlist Generator.
Ive selected the “Use Mirror Status” checkbox, so only active mirrors are included in the results.
To see the results, choose the “Generate List” button.
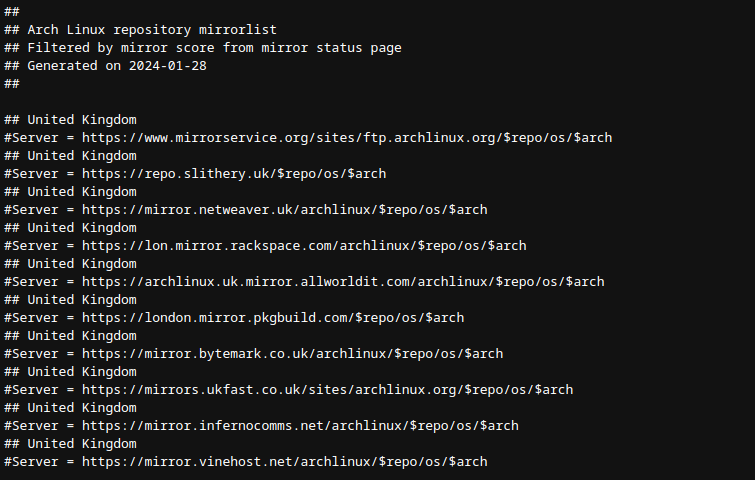
you could repeat this process for other regions, pasting the results to your editor each time.
I also selected mirrors in Germany and Sweden.
pacman reads its mirrors from a file called “/etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist.”

you’re gonna wanna edit that file and replace its contents with the new list.
Replace gedit with your favorite editor.
Copy and paste the list youve just created into the mirrorlist file, replacing the original contents.
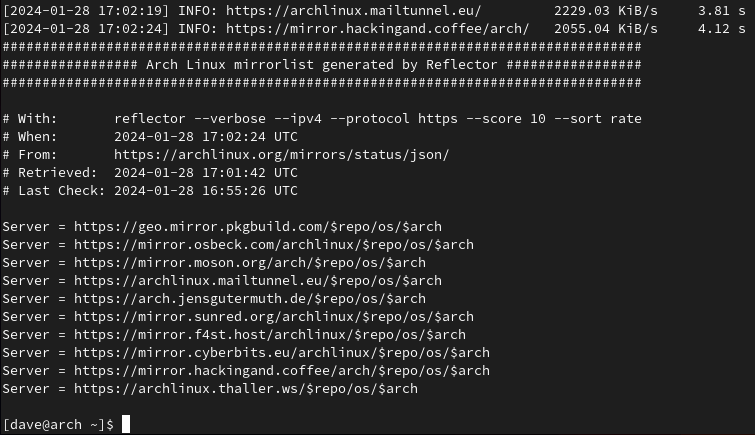
Save the file and close your editor.
pacman will now use our new list.
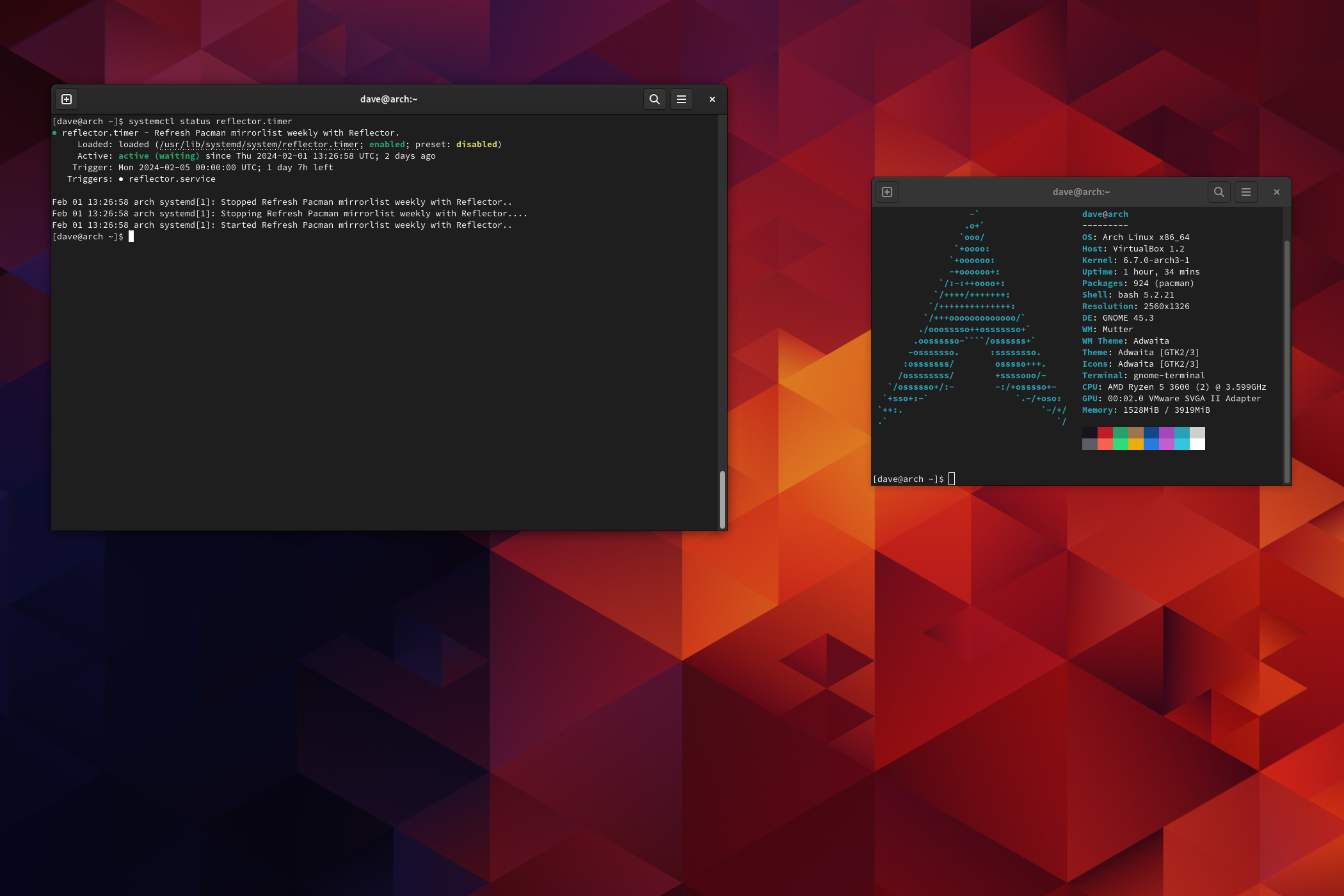
What Is Reflector, and What Does It Do?
Reflector is a utility for generating mirror lists, and optionally updating the mirrorlist file.
you’ve got the option to use it on the command line, or as a service.
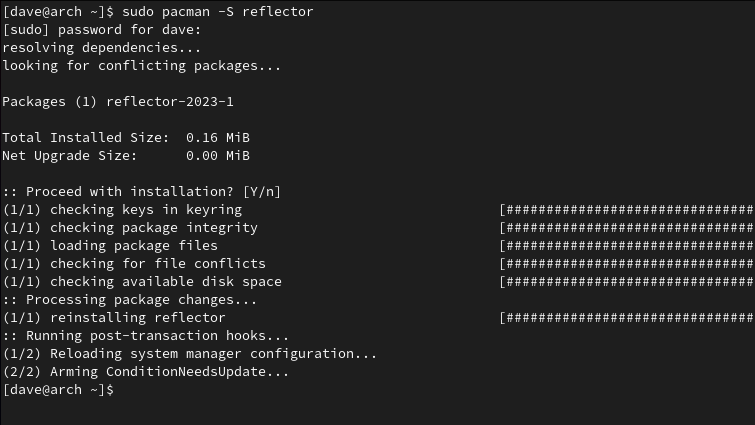
In Arch Linux, Reflector isnt installed by default, but in other Arch-based distributions, it might be.
If you dont, pacman wont work.
This exampledoesntoverwrite your mirror list.
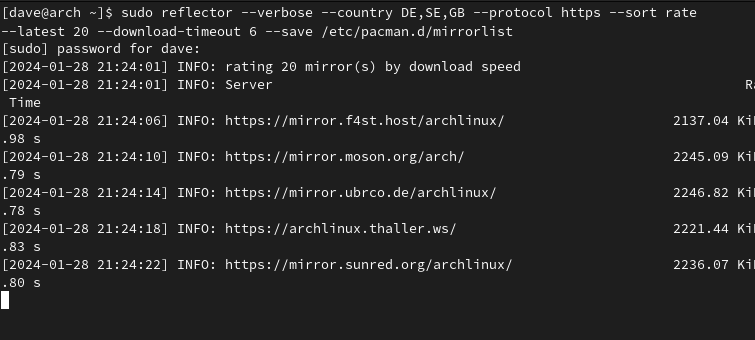
The options we used were:
Reflector supports a lot of command-line options.

Let’s include the –save option so that we update our mirrorlist file.
you better use sudo when using this option.
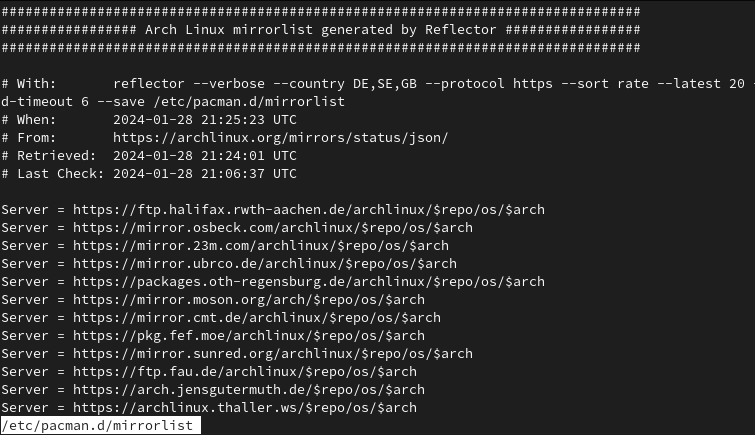
Reflector writes a timestamped header, so you’re able to see when the last update happened.
Using the Reflector Service
Reflector provides a service and a timer.
If you enable and start the reflector.service, itll tune up your mirror list whenever you boot your system.
The downside is slower boot times.
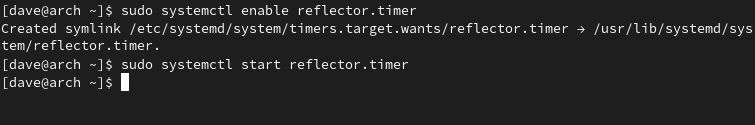
A better solution is to enable and start the reflector.timer instead.
Itll spin up the reflector.service once a week for you.
you might change their values or add in the ones you want to use.


