Quick Links
The Microsoft GraphAPI is a powerful tool to have.
In this article, we’ll learn how to explore and use the Microsoft GraphAPI for Azure AD.
Prerequisites
You must meet a few prerequisites before we can begin.
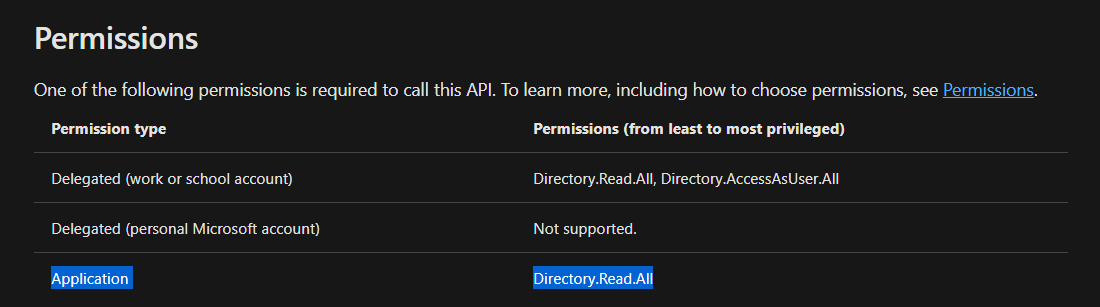
This specifies how to use a specific function and what permissions it’s crucial that you use it.
There are currently two versions of the GraphAPI: v1.0 and the beta API.
Also be aware that functions in the beta API are subject to change at any time.
The following screenshot shows the permission needed to use the
function.
And because you will access it as an software, you need the Directory.ReadAll permission.
It is this token that you must in the requests towards the GraphAPI.
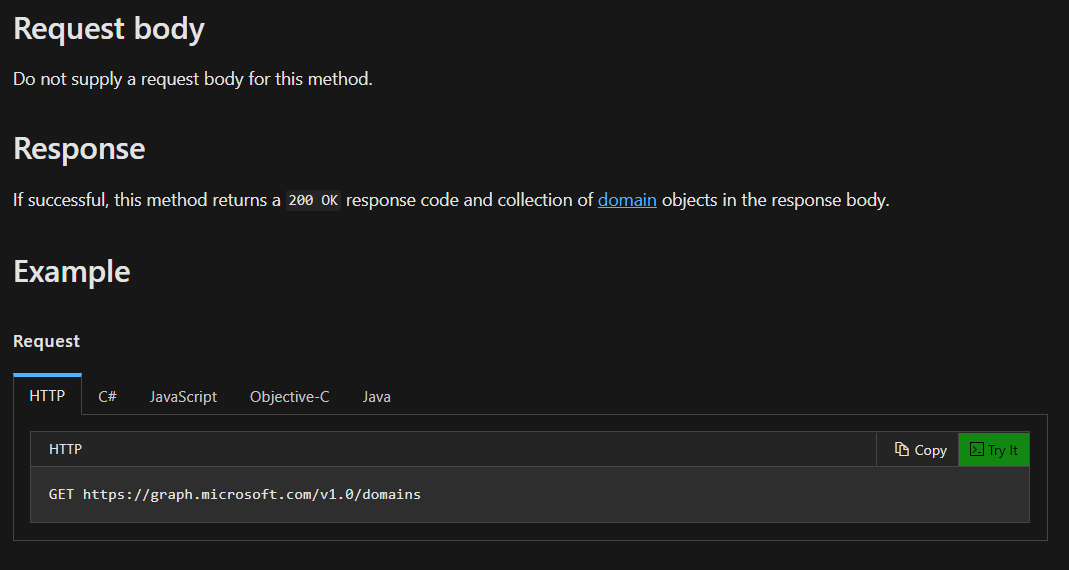
The simplest requests to start with are the requests that utilizes HTTP GET.
We will start out with a simple request listing the domains tied to our tenant.
And remember—read the documentation.
All information on how to use the GraphAPI functions is in thedocumentation.
Using Filters
It is great to be able to fetch all data that are available.
And while it may work, it is awfully ineffective.
A good practice is to only request the data that you need.
To achieve this in the GraphAPI, we can use filters.
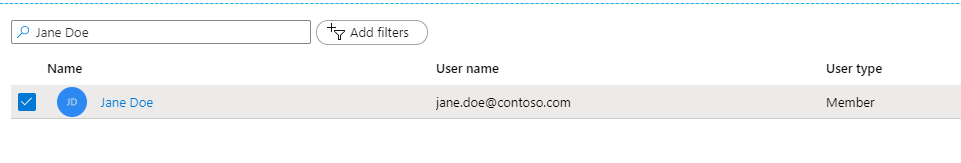
A good candidate for trying out filters is by fetchingusers.
you might do that by adding the $filter= parameter to the URI.
While out of the scope of this article, more information about operators is available in thedocumentation.
Also more extensive documentation about the different filter properties is available in the propertydocumentationabout each object bang out.
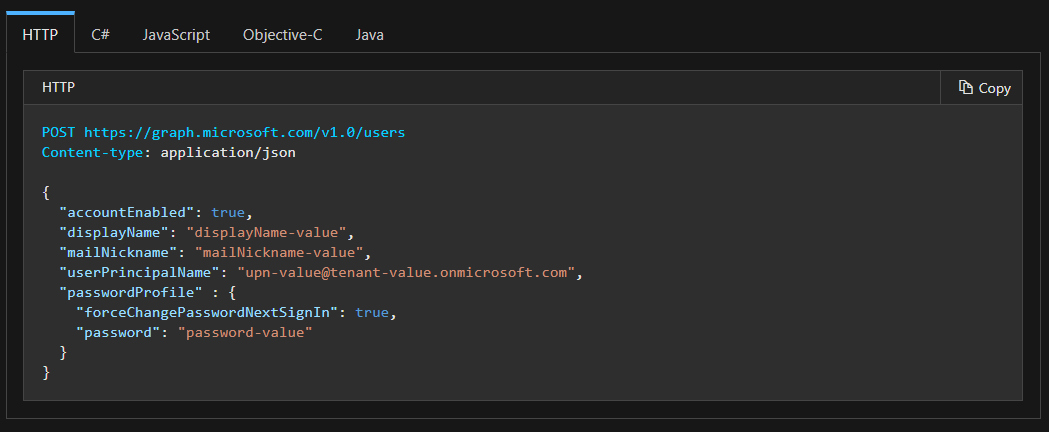
For that, you oughta know how to construct the data and where to POST it.
All without the need to include large libraries into your functions.