But what exactly are they, and why are they necessary or useful?
Lets take an inside look.
User Permissions
Back in the day, computers were massive machines that were incredibly expensive.
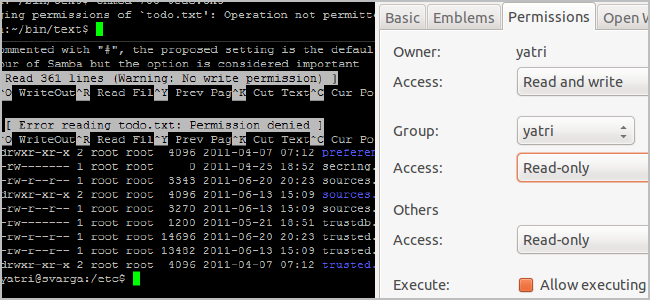
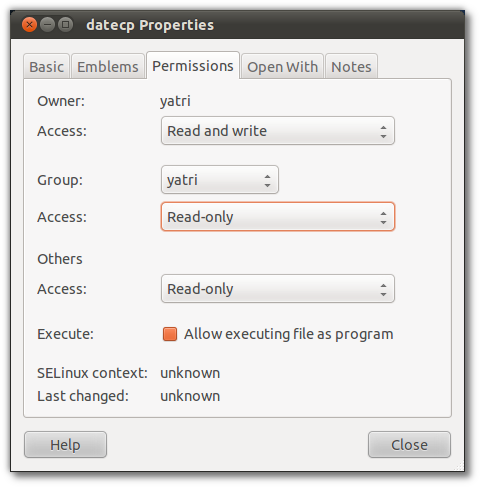
Each user is also placed into various groups, which grant or restrict further access.
But what about what they access?
Well, every file has a set of permissions and an owner.

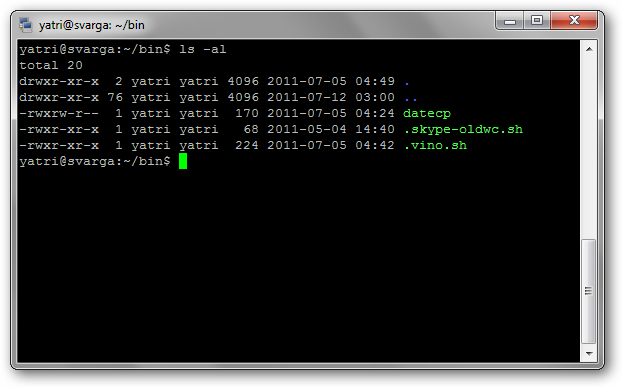
In the world of Linux, permissions are broken down into three categories: read, write and execute.
Each of these categories are applied to different classes: user, group, and world.
Folders can also be restricted with these permissions.
you might also create a shared directory that allows anyone to view and modify files in that folder.
Command-Line
it’s possible for you to also do this via the command-line.
It looks like this:
-rwxrw-r–
Therstands for read, thewstands for write, and thexstands for execute.
Directories will be start with a d instead of a -.
Youll also notice that there are 10 spaces which hold value.
you might ignore the first, and then there are 3 sets of 3.
To change a file or directorys permissions, lets look at the basic form of the chmod command.
First, lets look at the classes:
Next, the operators:
Still with me?
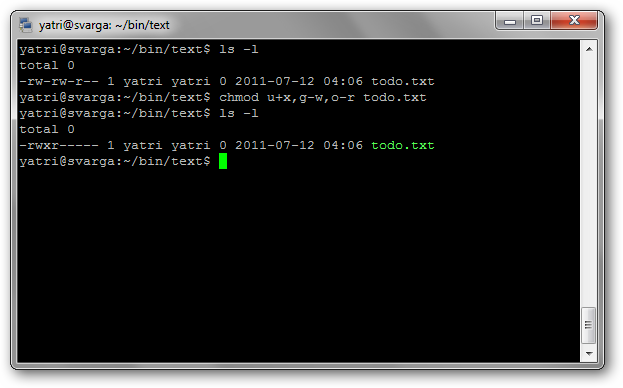
We can do this in 3 steps.
First, well add the execution permission for the user.
chmod u+x todo.txt
Then, well remove the write permission for the group.
chmod g-w todo.txt
Lastly, well remove the read permissions for all other users.
Why should we still worry about permissions?
As such, things that are integral for the system need admin privileges to be changed or accessed.
This way, you dont mess up anything accidentally.
File permissions are in place to provide a basic system of security amongst users.