The truth is, the speed is only a single factor in overall CPU performance!
Discover how fast your CPU really is.
How Fast is Your CPU?
What matters most is the actual and overall performance of the CPU.
One important factor besides processor speed, for example, is the number of threads.
you might picture a thread like tube.
Shutterstock/Rost9
If you have a single threaded processor, it has a single tube through which to pass water.
If you have a double threaded CPU, it now has two tubes.
The main two CPU brands are Intel and AMD.

Still, that is not all there is.
Next up is caching.
A CPU has multiple levels of caching.
Often these are called L1, L2, L3 etc.
(level 1, level 2, level 3, etc.)
One can think of these like buckets that fill up, and overfill.
The L1 cache is ultra fast and closest to the core.
Still, that is not all there is.
Bus / channel width is another consideration.
The bus is a mechanism by which the CPU communicates with devices and main memory.
Whereas the term multi-core (multiple cores) may be used in this context, it is somewhat misleading.
Using a dual slot CPU mainboard willtend towards doublingthe CPU processing power of your workstation.
all contributing to the actual performance of a dual (or more) CPU system.
Slight manufacturing and ground material differences may make for a slightly faster or slower version of the same CPU.
Let’s explore how fast our CPU really is.
Such a list exists.
For a modern fast workstation, you will want to look at least at a 8000 CPU Mark.
And higher for servers.
Server based CPU’s are also benchmarked and on the same list.
I would be too.
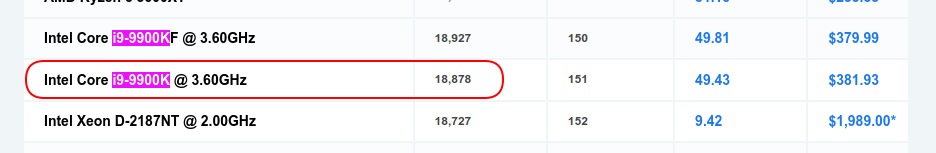
The next match shown is ‘Intel Core i9-9900KF @ 3.60GHz’.
Almost, but not exactly the same (notice the additional ‘F’).
Think about it like installing a Ferrari Engine in a Jeep car.
The car may drive (if you have a handy mechanic!
Wrapping Up
Before buying that next CPU, review it’s performance!
Before committing to a dedicated server for your business, review it’s performance… bus bandwidth, L1-L2-L3-Lx cache, number of threads and cores, etc.)