Here’s how to go about it in Windows 10 and Windows 11.
What Are Routing Tables?
You’ll probably see PowerShell instead of Command Prompt in the Power Users menu.
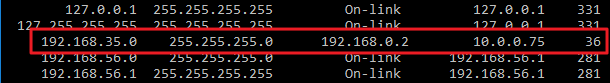
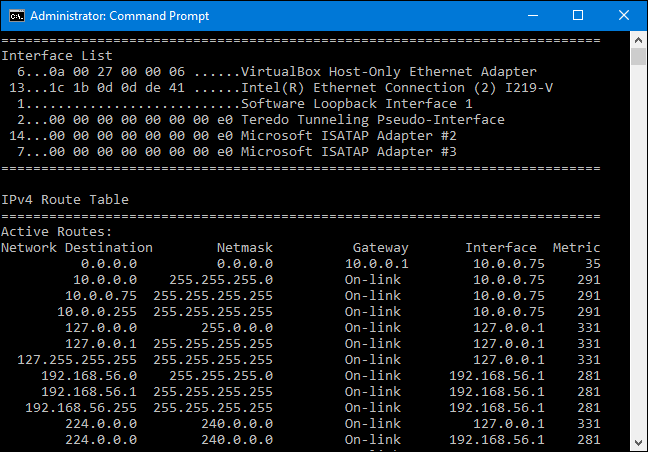
Unless you’ve already added static routes to the table, everything you see here will be dynamically generated.
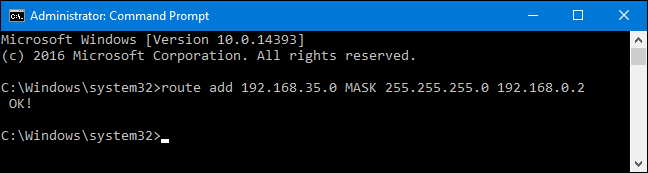
If you don’t specify a subnet mask, 255.255.255.0 will be used automatically.
That’s all easy enough, but there is one extra little catch.
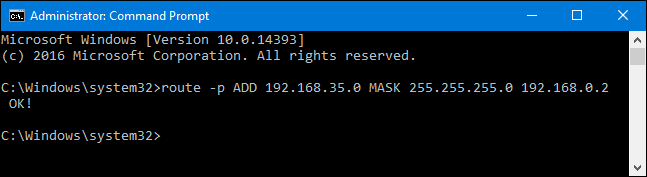
When you add a static route, by default it only lasts until the next time you start Windows.
This keeps the routing table relatively uncluttered.
You could certainly use the batch script method yourself.Writing batch scriptsisn’t hard.
A persistent route stays in place even when Windows starts up.
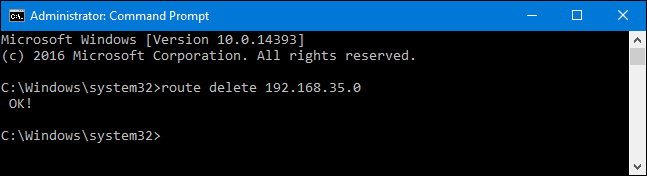
But if you do need to do it, it’s a pretty easy process.