Related
Quick Links
A swapfile is used by Linux when processes run out of memory.
What is a Swapfile?
Let us start by a rhetorical question: what happens when your setup runs out of memory?

This can lead to painful results like data corruption or unavailable services.
Not directly, and there is processing overhead, but indirectly and with considerable processing speed impact.
Swapfile Advantages and Disadvantages
Main memory is usually ultra fast when compared with slower disks.
Even SSD’s (solid state drives) are almost always slower then high-speed main memory chips.
The delay of writing data back and forth between main memory and disk (i.e.
This will be very noticeable.
Shutterstock/ Mbok Menawa
It has the same the target functionality is the same as that of a swapfile.
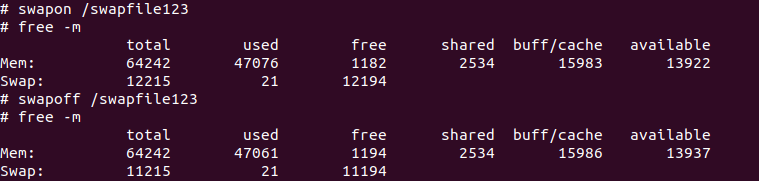
you might also see how only a small amount (23.5M) is currently in use.
If you suspect your system is swapping, check how these two counters look.

If they are both near-full, your system is highly likely swapping heavily and will run significantly slower.
The reason is that now there is a heavy I/O bound (i.e.
disk bound) load, constantly swapping main memory with disk based memory.
I personally take another route, and that is to consider how much additional memory I may need.
How to Enable a Swapfile
Ready to add a swapfile?
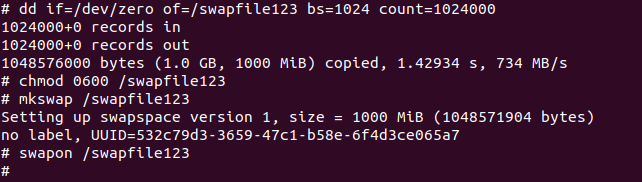
This can be done on the fly.
We usesudo suto enter superuser (su) mode viasudo.
You should see output similar to the following:
If so, congratulations!
Next we set some appropriate security privileges.
We next indicated to the operating system that the file was to be made a swapfile using themkswapcommand.
Finally we turned on the swapspace, dynamically at the command line, without having to restart our system.
you could also see how we usedswapoffto dynamically turn off swap at the command line.
We now only have one small issue to address.
No setting change was made so far which will ensure that the swapspace is reloaded on system reboot.
Do not modify or delete any other lines as this may result in your system not booting correctly anymore.
Also ensure to double check the contents of your /etc/fstab file before restarting by executing thecat /etc/fstababove.
you might now reboot your system and confirm that your extra swap space is still available by usingfree -magain.
Do not modify or delete any other lines as this may result in your system not booting correctly anymore!
you’re able to then execute:
All done!
No need to reboot either, as this change was made dynamically.