Here’s how to find these applications and speed up your gear.
To access Task Manager, press Ctrl+Alt+Del and select “Task Manager.”
On Windows 10, switch to the “Startup” tab at the top.
Jason Fitzpatrick / How-To Geek
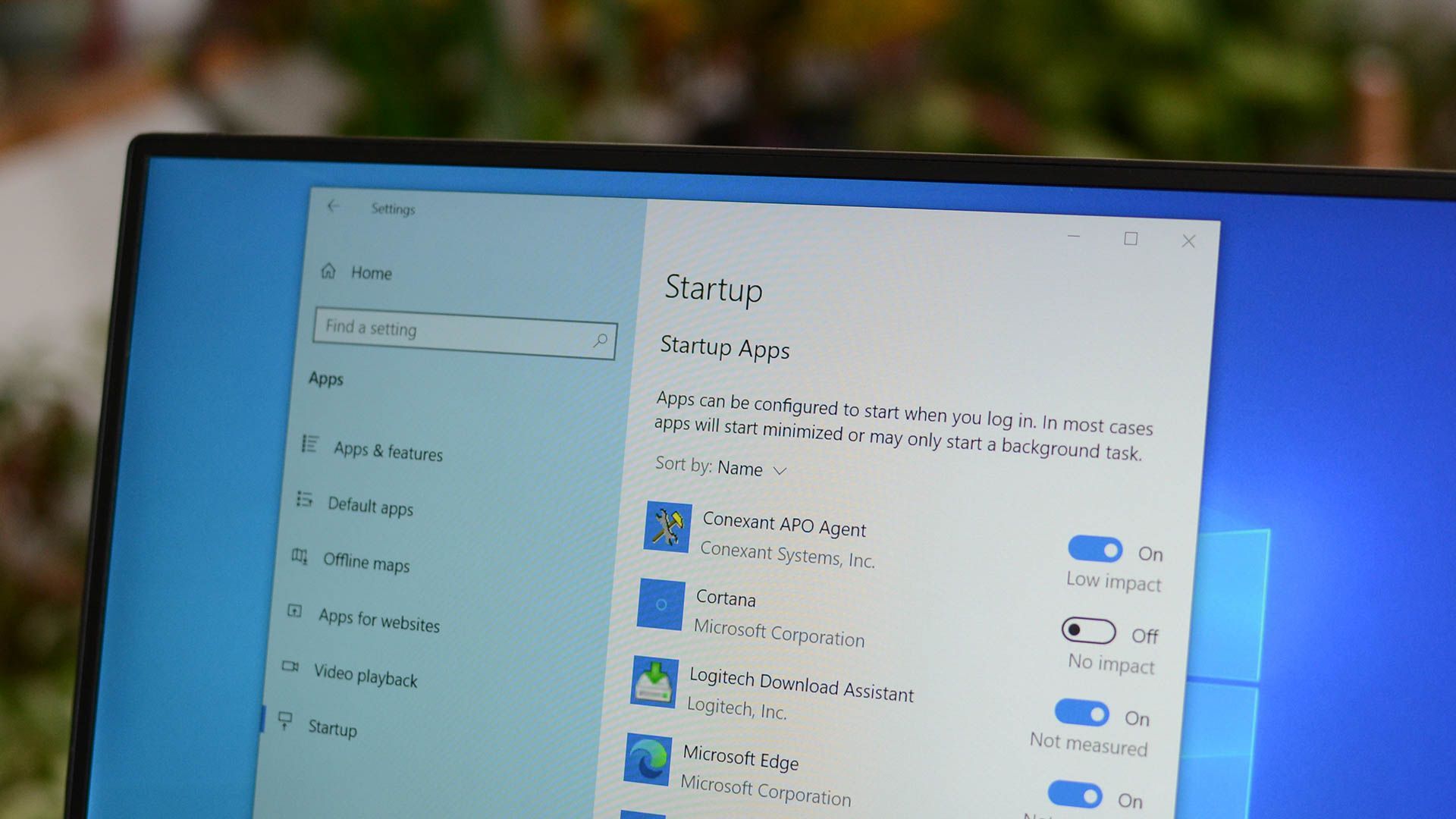
On Windows 11, select “Startup apps” from the left sidebar.
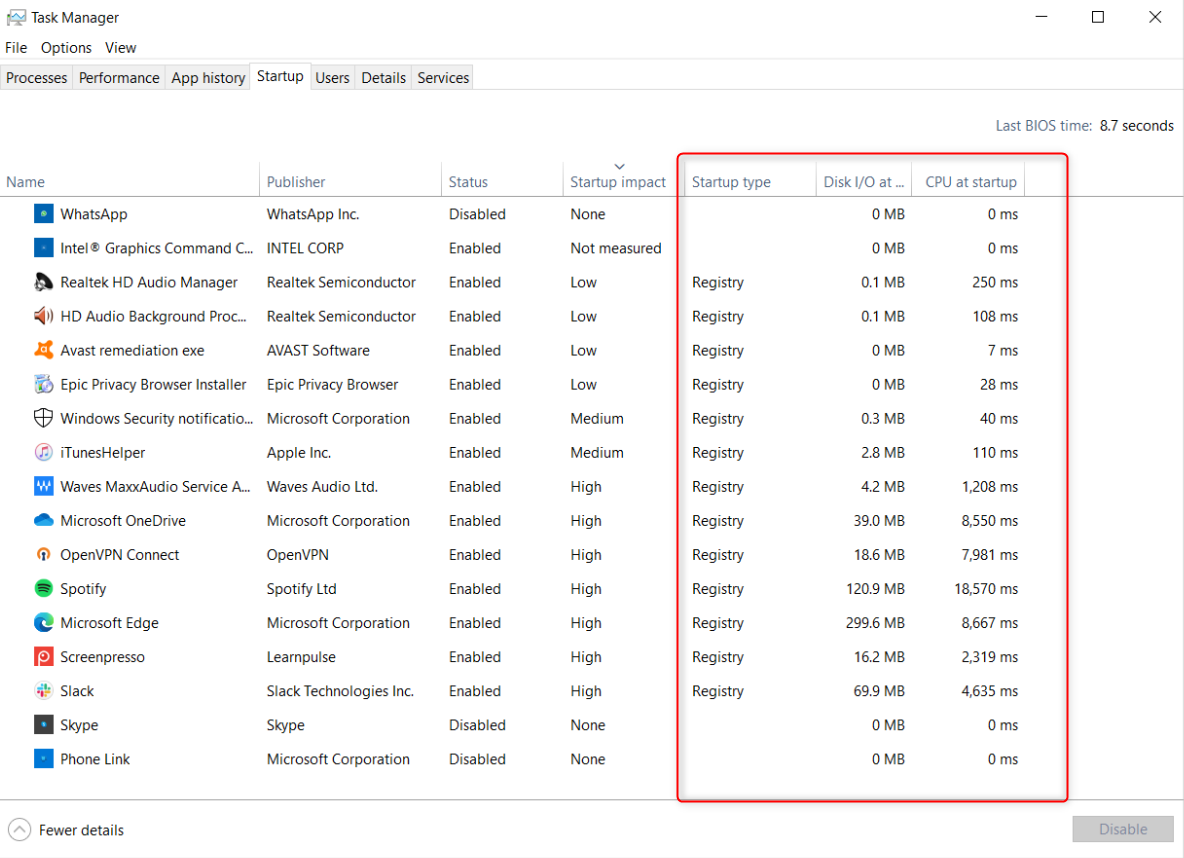
Each row lists an software alongside details relating to the startup.
But if you rarely use these programs, you don’t need them slowing your startup.
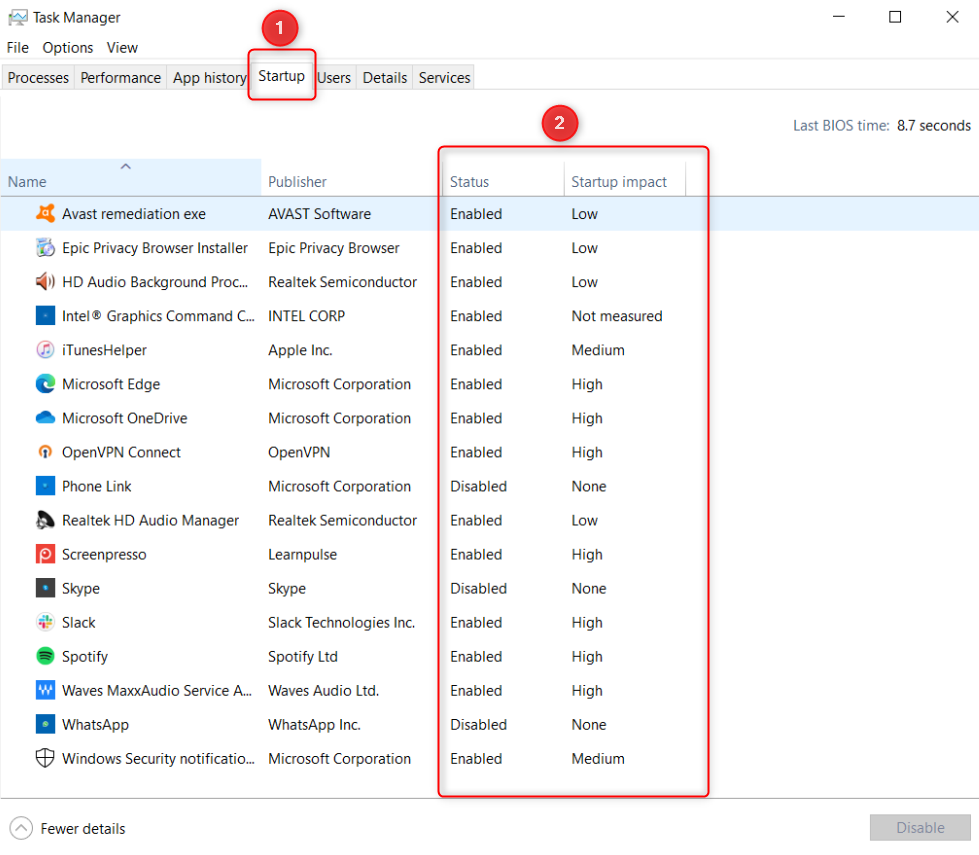
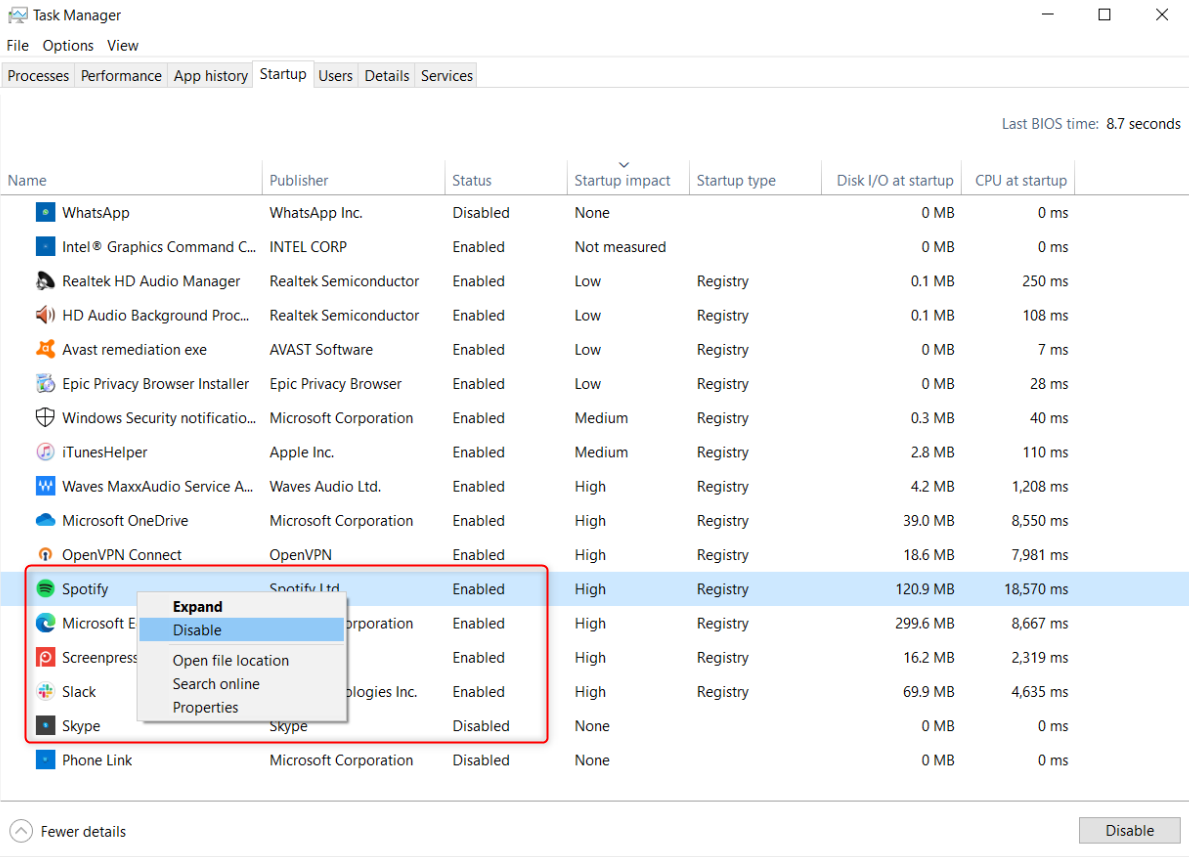
To remove a program from startup, right-click it and select “Disable.”
Don’t be deceived by the “Last BIOS Time” in the top-right of Task Manager.
It’s impacted by factors like the hardware you have connected, rather than your startup programs.
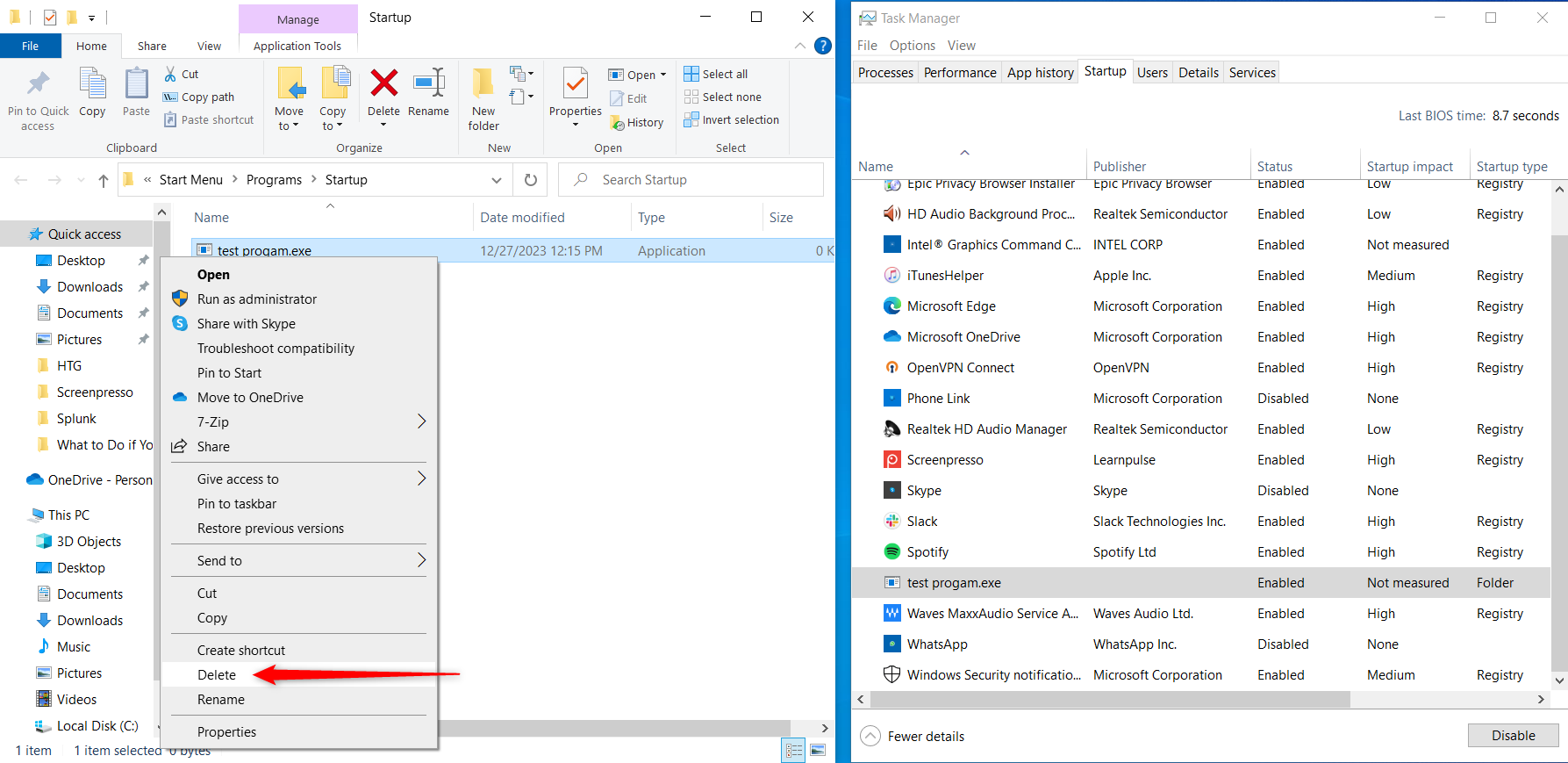
The folder may also contain scripts and shortcuts that may not appear in Task Manager.
Only delete something from your startup folder if you’re certain you don’t need it.
If you have multiple users on your machine, each individual will have different startup folders.
There’s also a general startup folder for the whole PC.
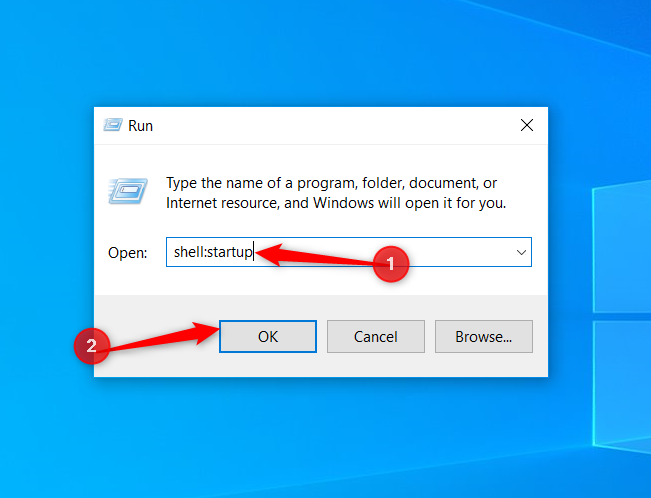
To reach the startup folder, first press Win+R to open Run.
If that’s the case, you have no action to take.
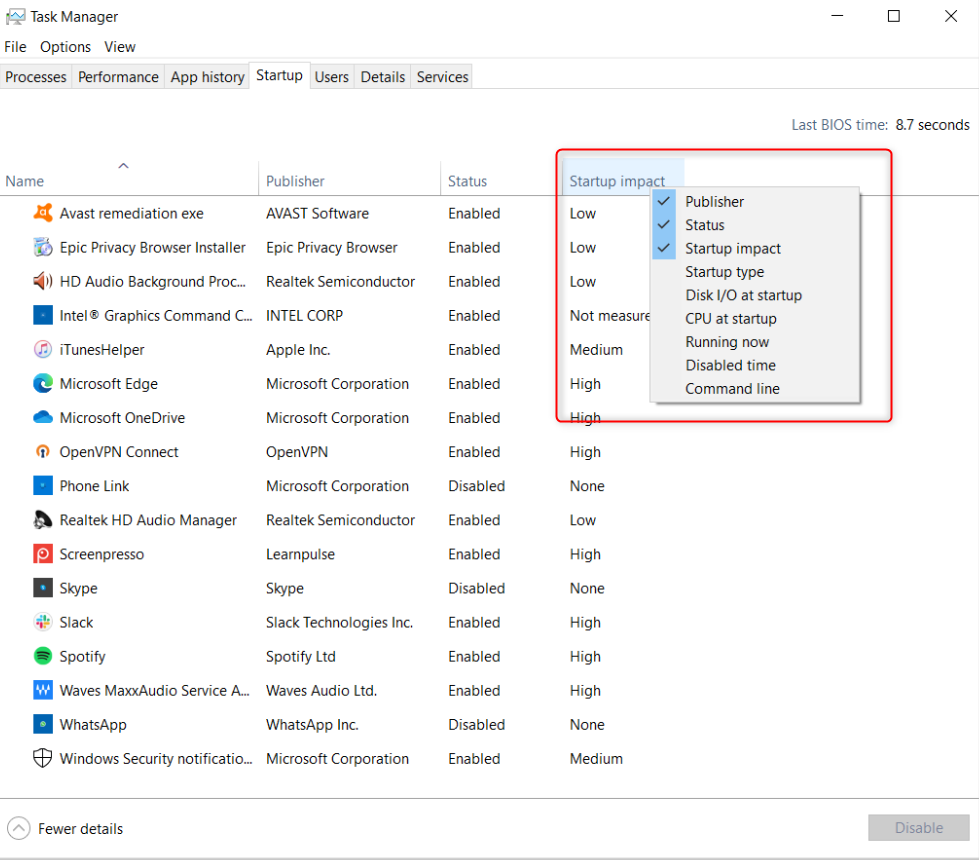
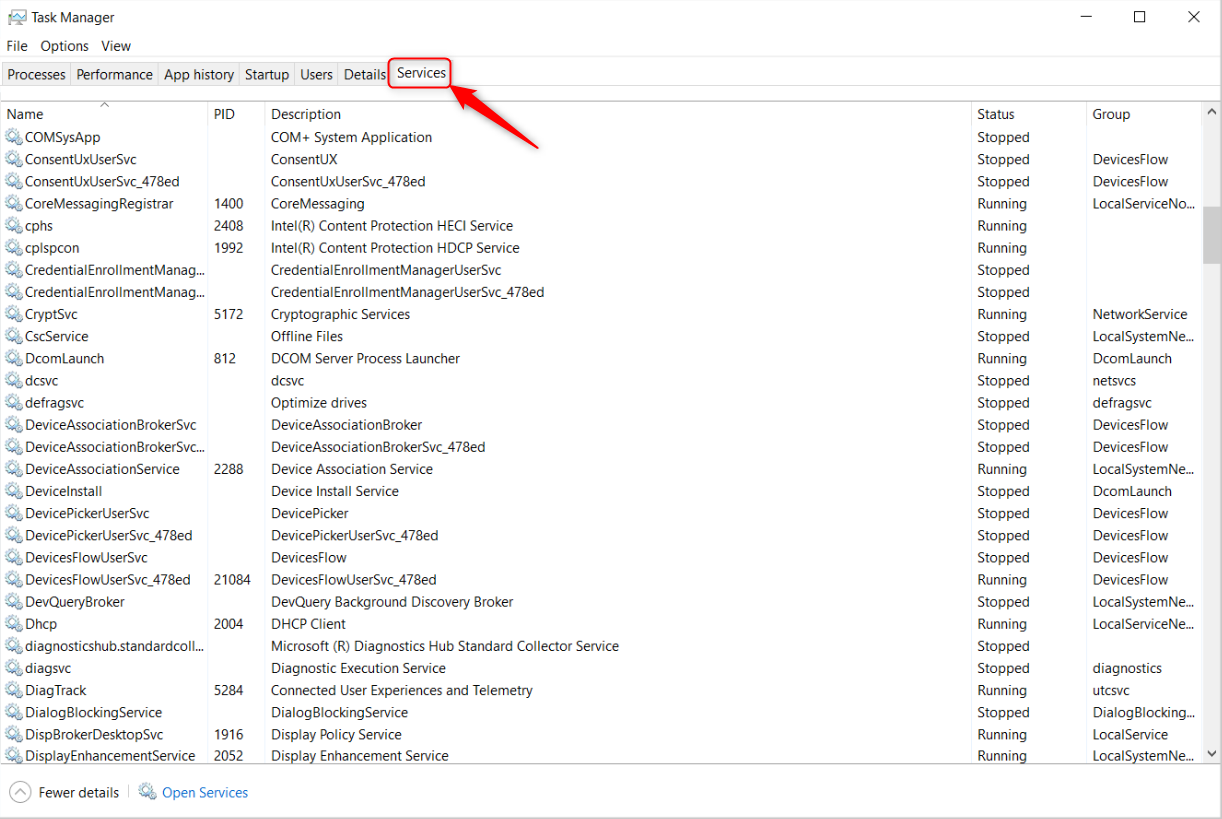
However, you could see them in Task Manager.
Do not change or turn off anything if you don’t know what it is.
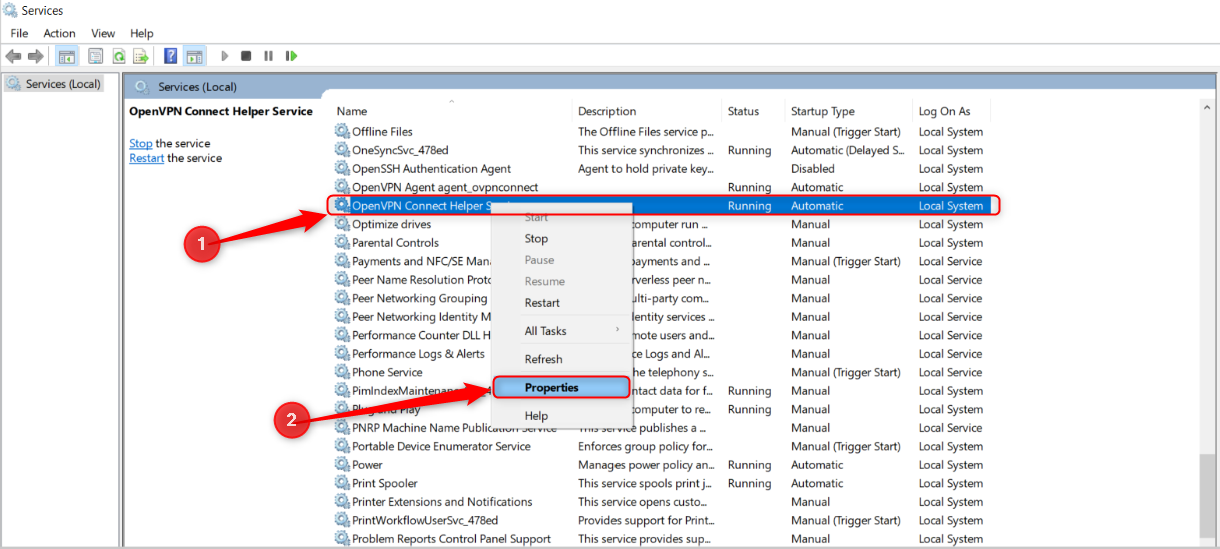
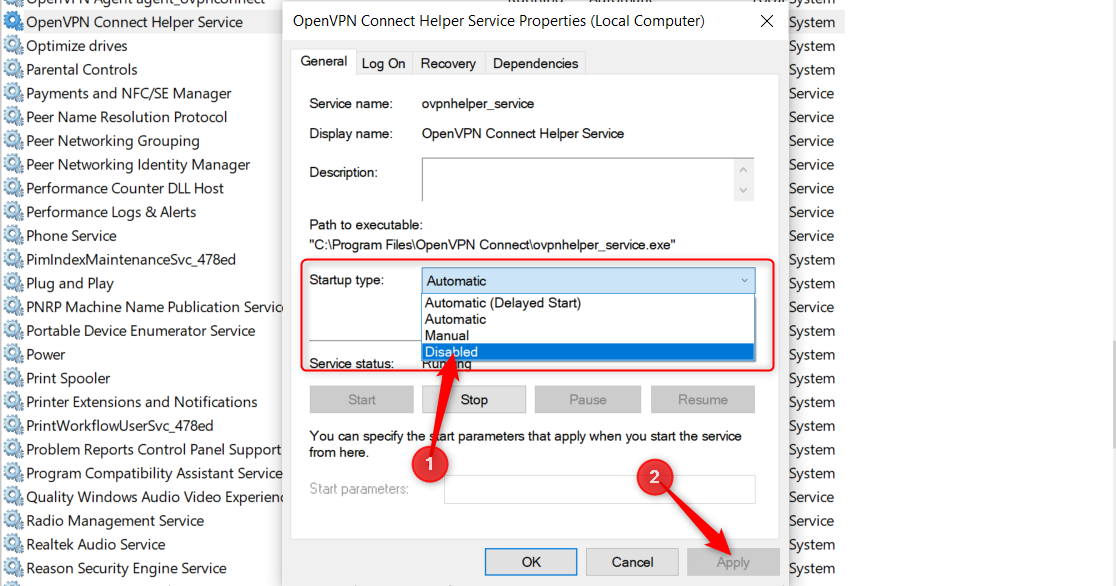
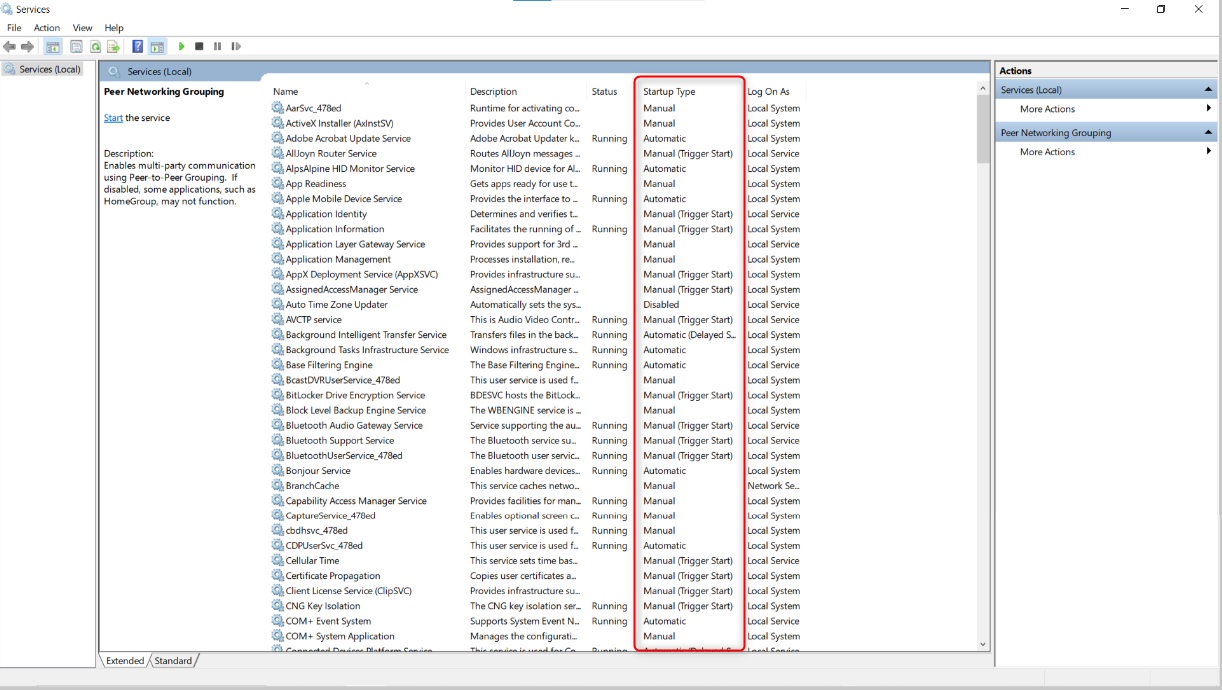
On the list of services, look at the Startup key in column.
Right-smack the service you want to modify and select “Properties.”
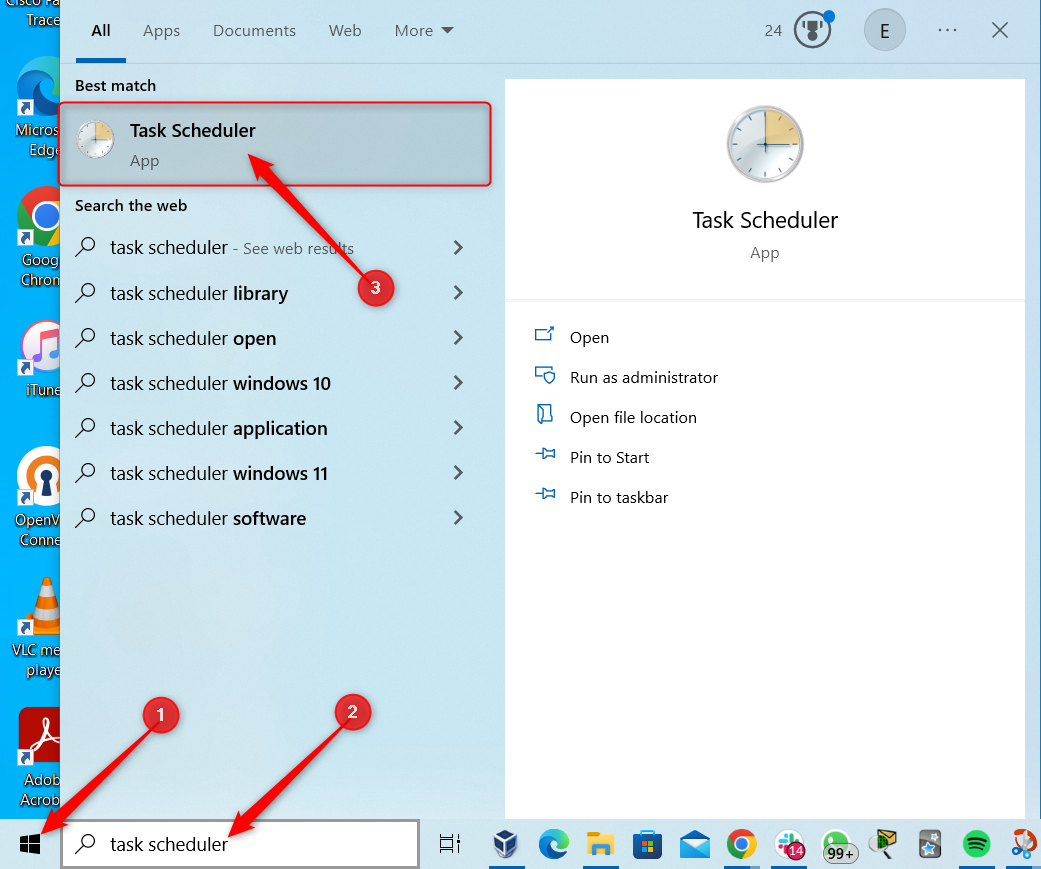
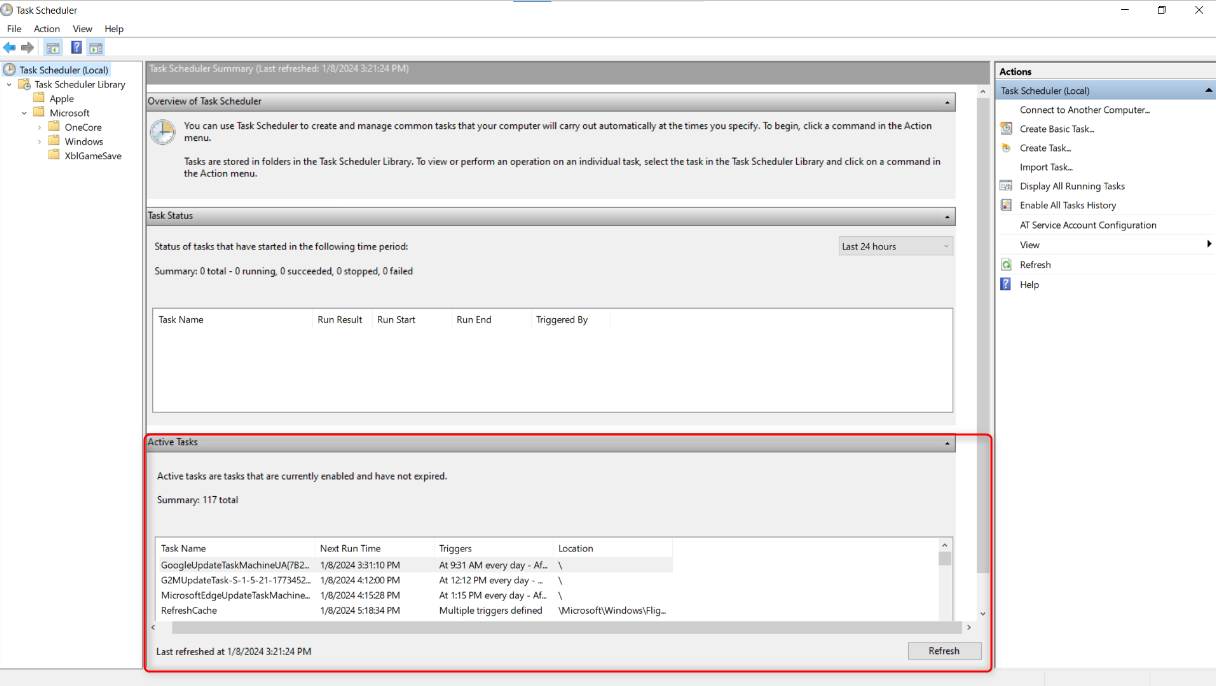
To begin, search for and open Task Scheduler through the Start menu.
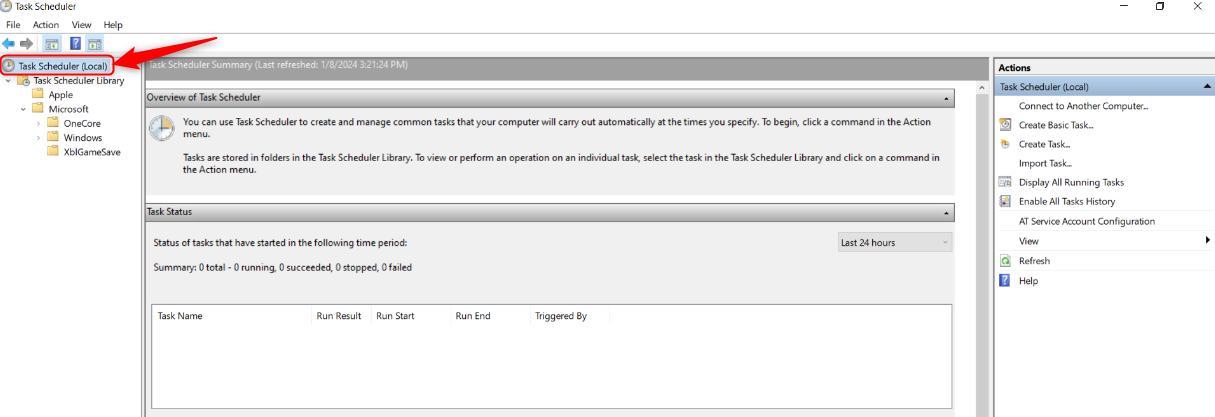
In the left pane, click “Task Scheduler (Local).”
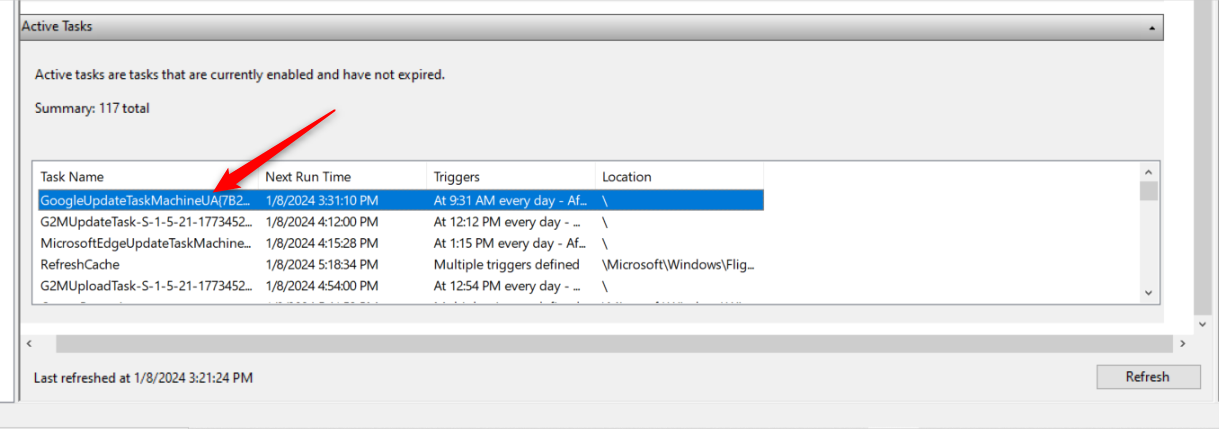
Click “Refresh” if it’s outdated, to show the most recent tasks.
Double-punch a task to open it and view more details.
Use the information herein to decide whether you gotta disable a task.
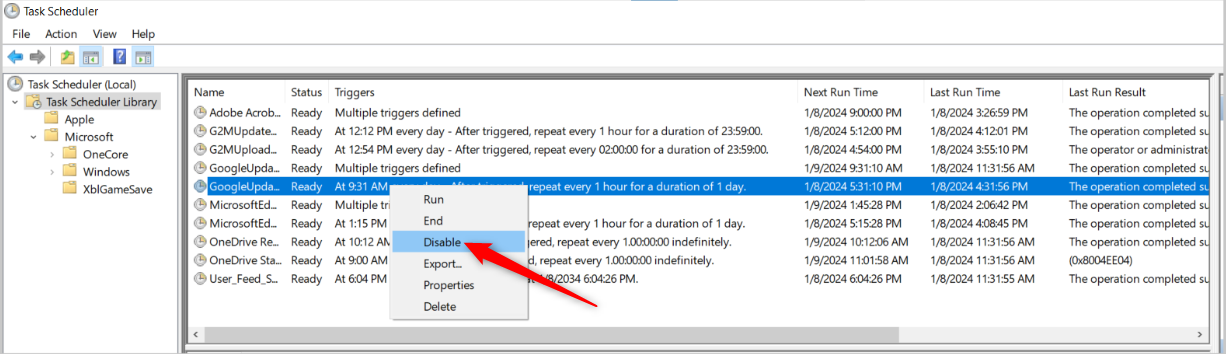
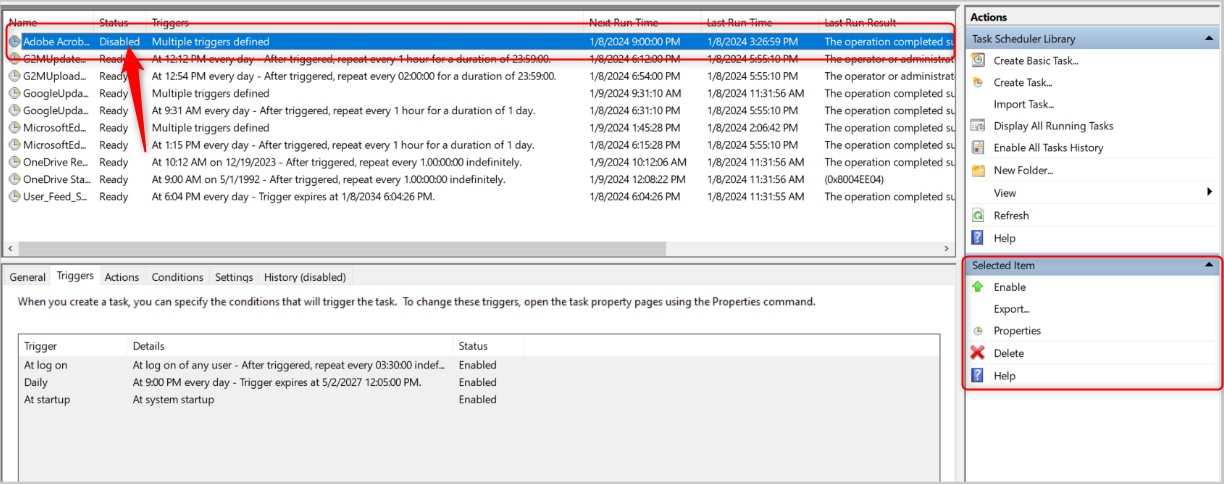
To kill the task, right-click it and select “Disable.”
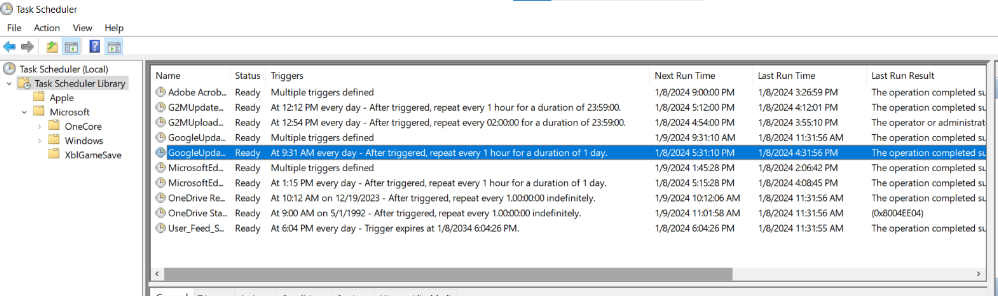
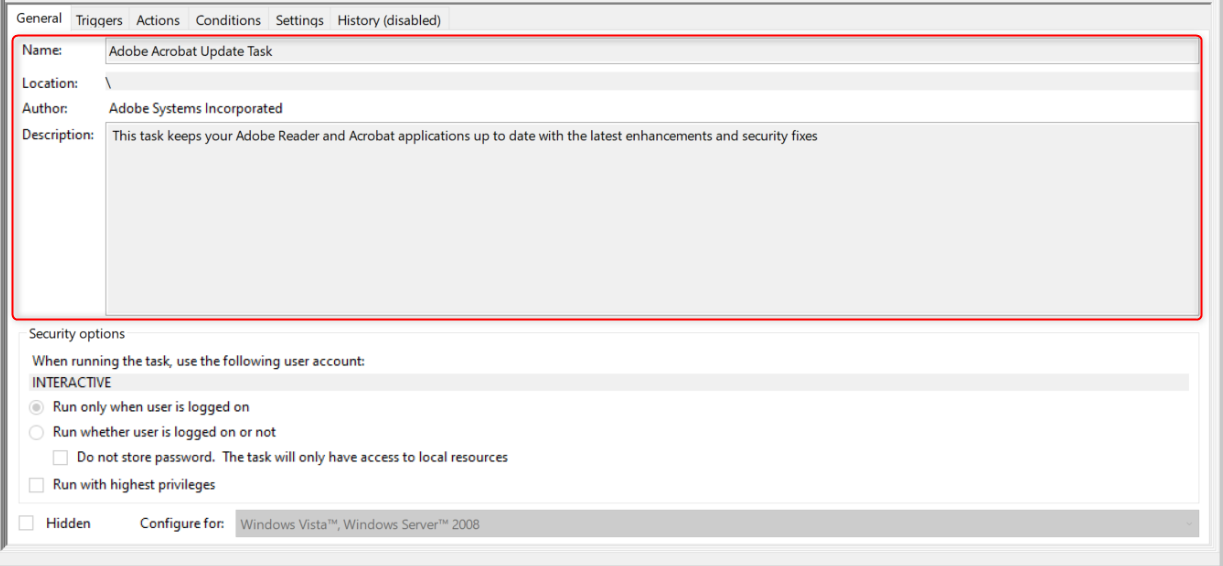
The “General” tab provides the task name, location, and description.
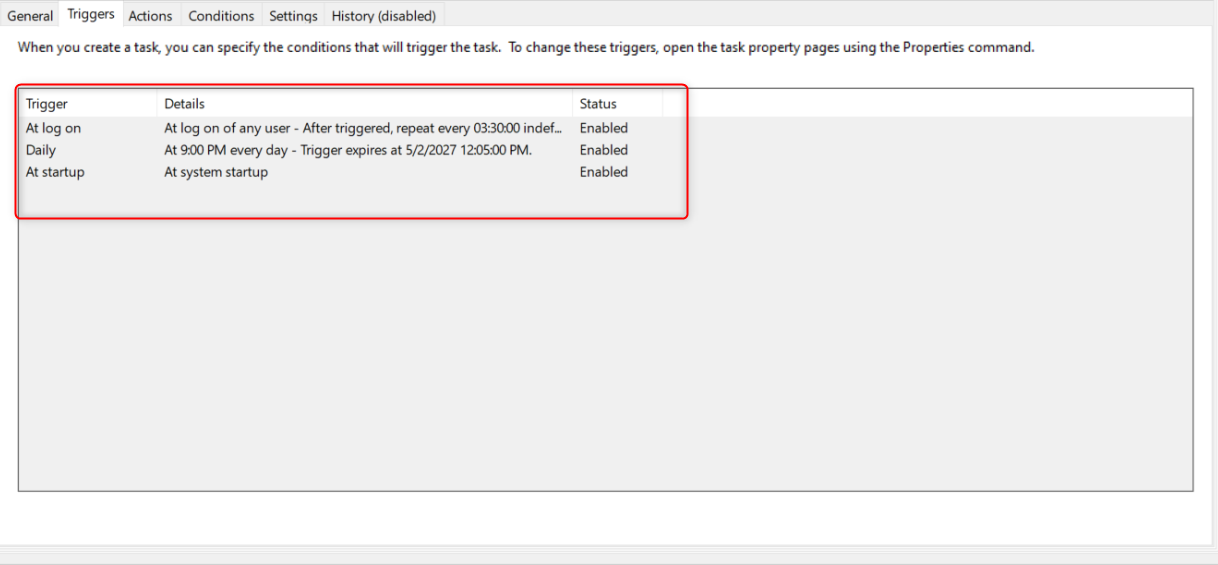
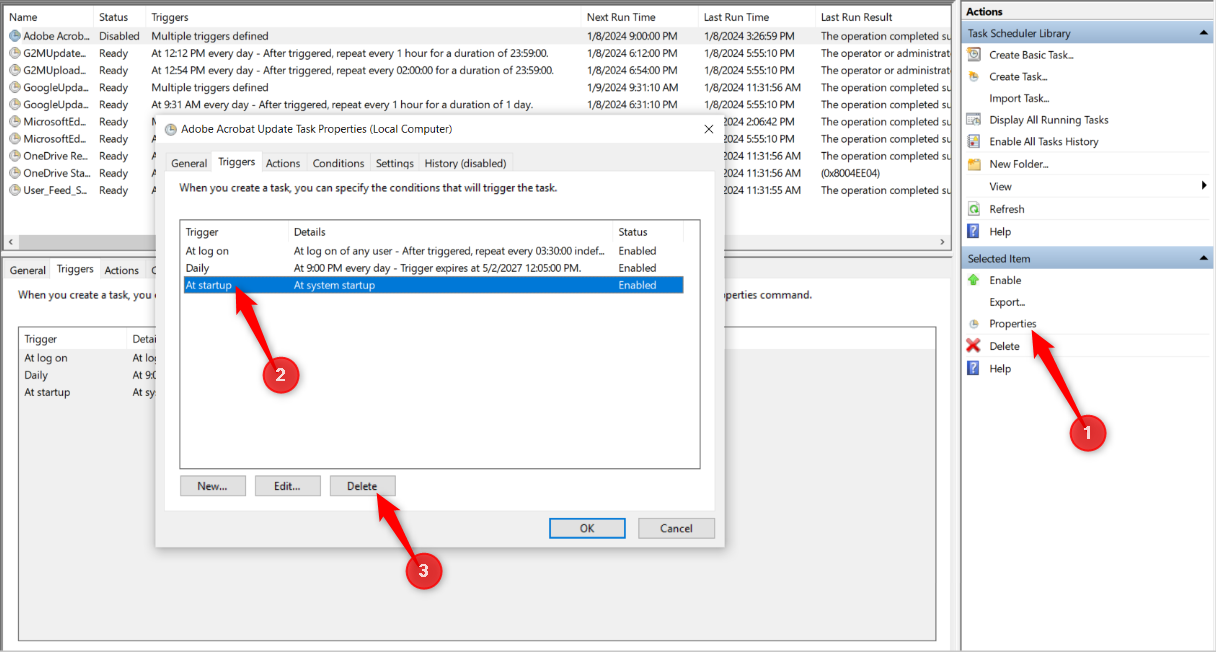
The “Triggers” tab shows what conditions will activate the task.
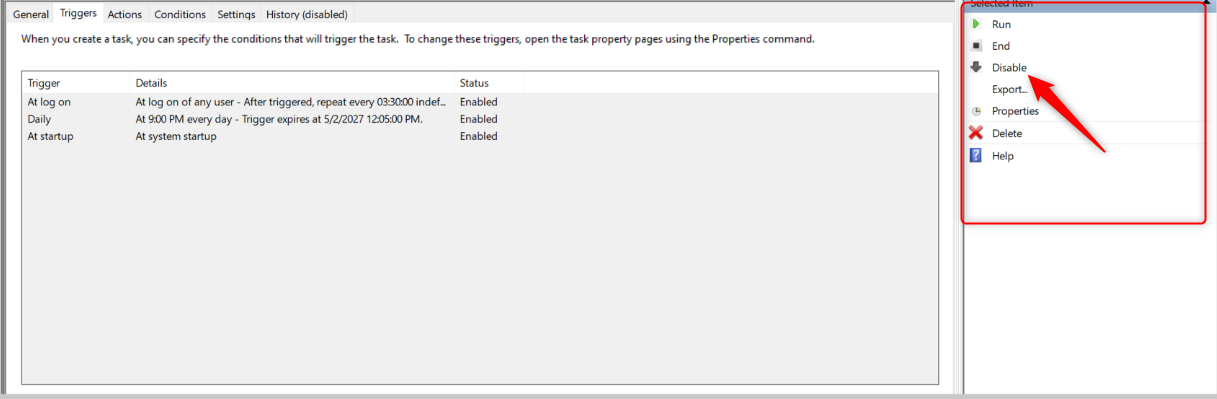
To disable it completely, click “Disable” in the right pane under “Selected Item.”
The second option is to modify the triggers.
initiate the “Triggers” tab, pick the desired trigger, click “Delete.”
Click “OK” when done.
That’s itthe task will not start with the PC.
If you still experience a slowdown, there might be more to the issue.