Summary
Every year, the Python programming language receives major updates and improvements.
But the version preinstalled on Ubuntu Linux may not be the latest.
For this tutorial, we’re using the Ubuntu 22.04 LTS version.

Hannah Stryker / How-To Geek
For demonstration, we will install Python 3.12, which was released on October 2, 2023.
But this guide is applicable for older versions of Ubuntu and any upcoming Python releases.
Just to be sure, you might ensure it’s installed bychecking its current version.

That also shows you which version is installed and whether it’s already in its latest version or not.
To compare your results, you’ll find all the version numbers and maintenance statuseson the official Python website.
Step 2: drop in the Latest Python Version on Ubuntu
We’ll cover two methods here.
If you want a quick and simple method, go with the first one.
If you’re more comfortable building software from source files, use the second method.
you oughta add such repositories to your repo list first.
Then you’ll be able to install any software from that repository.
For the latest version of Python, we’re going to usedeadsnakes PPA.
It contains many versions of Python.
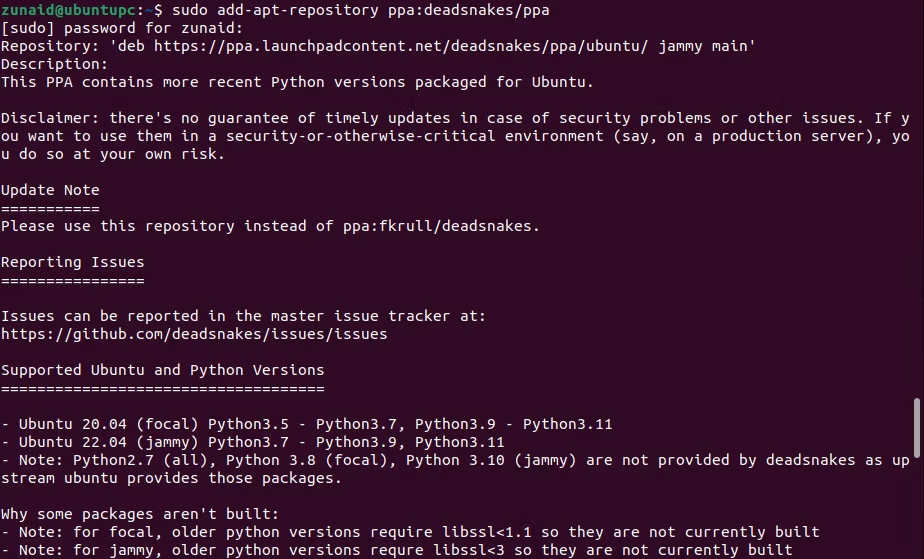
To add that repository, use the below command:
When asked to confirm, press the Enter button.
To make the changes take effect, you oughta tune up your software repository cache.
So update it with this command:
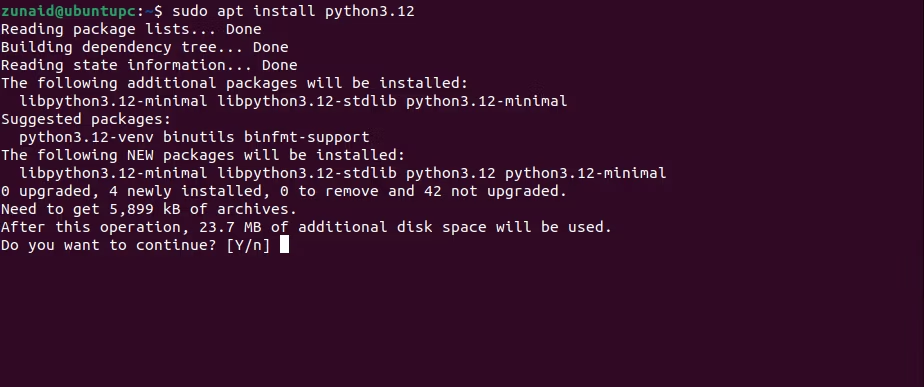
Now you’re ready toinstall software from the PPA.
Wait until the installation is finished.
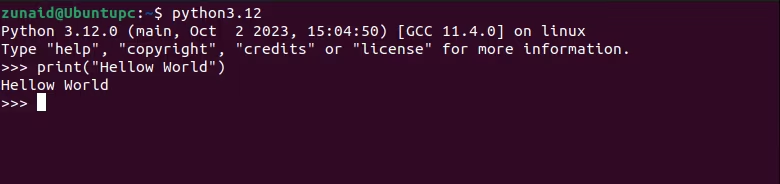
After the installation, you could start using the new version right away.
For that, you should probably use the version number when choosing Python.
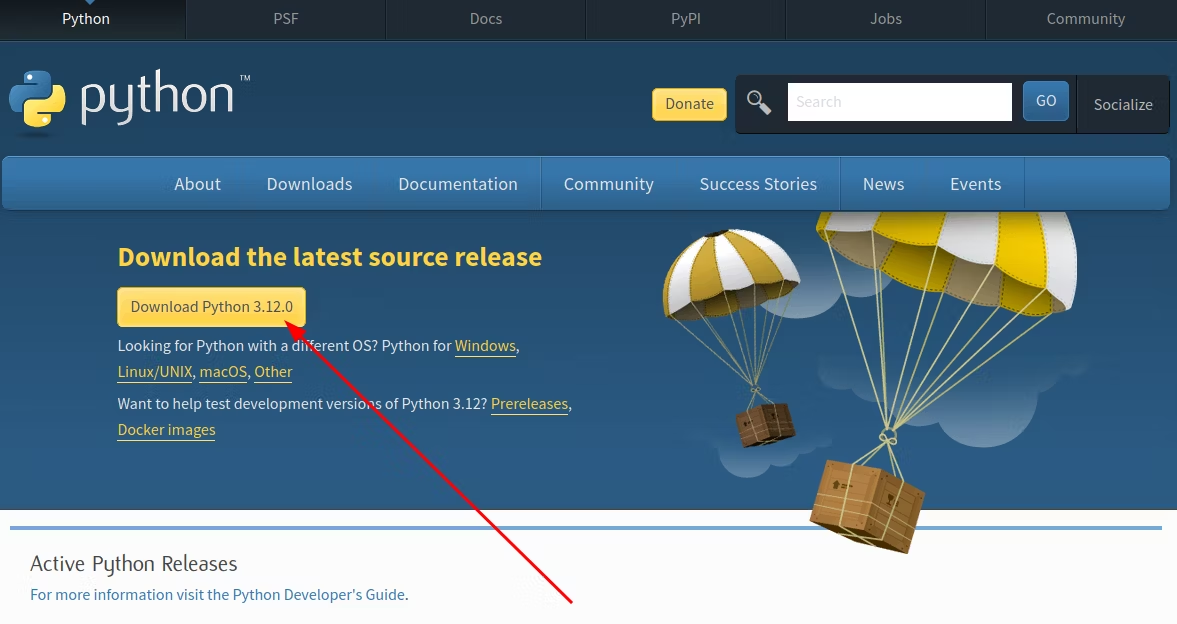
So now, go tothe downloads page.
Then press the “Download Python ” button to start the download.
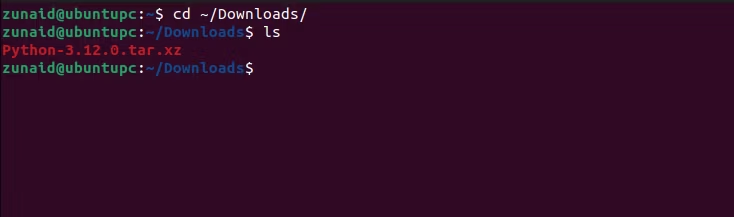
Open your terminal and navigate to the location where you downloaded the file.
By default, it’s the “Downloads” directory.
Go to that directory with this command:
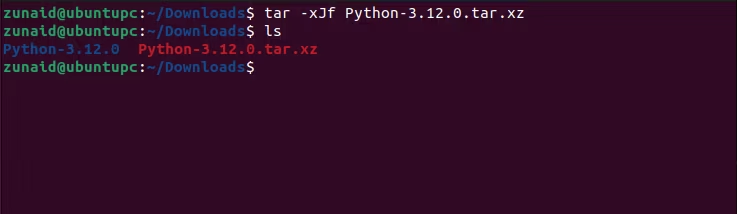
The source file is an XZ compressed source tarball file.
You need toextract this tar file first.
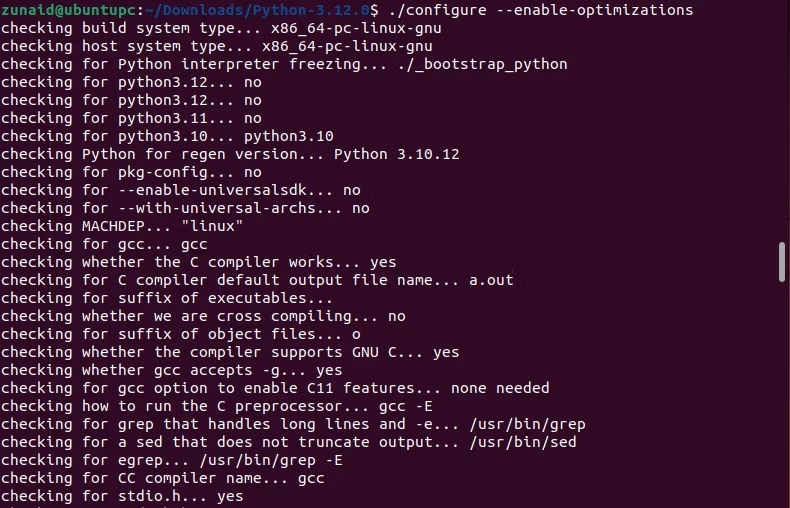
For that, we’ll use the provided “configure” script.
The script will create the necessary Makefiles for us.
Use the generated Makefile to build Python with this command:
This will take a while so wait patiently.
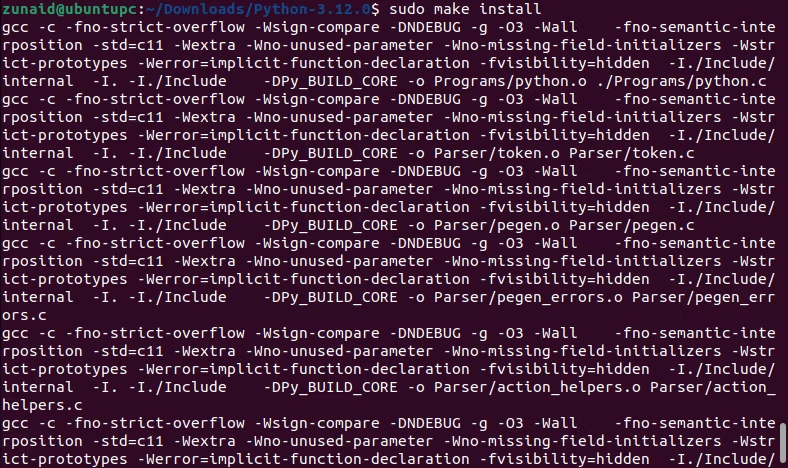
Once the process is done, you should have the installed version as the default one on your rig.
Your system is still using the old version.
you could verify that by checking the version again.
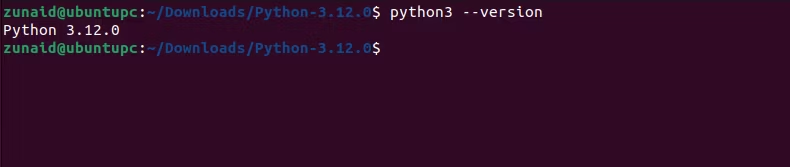
it’s possible for you to do that using the update-alternatives command.
Let us show you how.
We will specify the path to the newly installed Python for the python3 command we use.
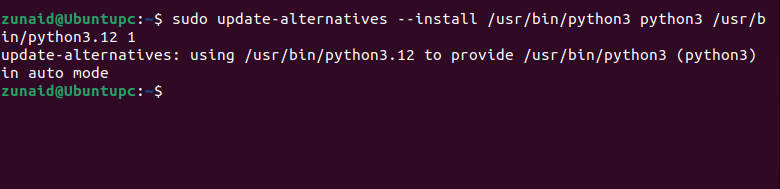
This saves you from any conflict because the higher the priority number, the higher the precedence.
But, if there are several versions in the group, you better pick the new version.
For that, trigger the below command:
Notice the numbers under the “Selection” column.
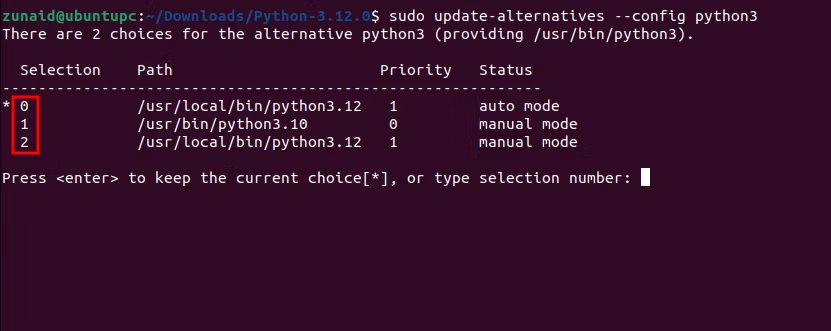
Enter the order number for the Python version you want to use.
Then press the Enter button.
Now you should be using the latest Python version on Ubuntu.
Check the version to confirm one last time.
Should You Upgrade to a New Version of Python?
So it might seem logical to update to the latest version.
And in general, that’s totally fine.
But it does come with some catches.
So you’ll need some getting used to before it becomes normal again.
Some packages may not support the new version right away.
Even worse, some new versions can break your existing projects and make a mess.
So you must be careful with that.
So, it comes down to your needs and preferences.
it’s possible for you to also usepyenvto switch between versions when working on different tasks.
Remember to read therelease notesand theofficial documentationto learn more about that version.
Interested in installing Python on platforms other than Ubuntu?
Check out our comprehensive guide onhow to install Python on Windows.