In this article, Ubuntu is the distribution of choice, notably that of 18.04.
Instructions for other distributions are locatedhere.
There are two main packages we need to install for rsyslog.

Beyond the base package itself, thersyslog-gnutlspackage allows us to use an encrypted connection to the Loggly service.
Configuring Loggly
Over time, the configuration directives and syntax have changed for rsyslog.
Often, there is a mix of the old and new directives available.
Below is a default configuration for rsyslog using the new syntax only.
The primary reason to modify this configuration is to point rsyslog to the certificate that we just downloaded.
The important part of the code is thedefaultNetstreamDriverCAFileanddefaultNetstreamDriver.
These directives need to be configured correctly to point to the downloaded certificate.
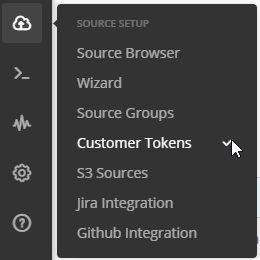
After signing in to your Loggly account, you will need to create a customer token.
This is located under Source Setup > Customer Tokens.

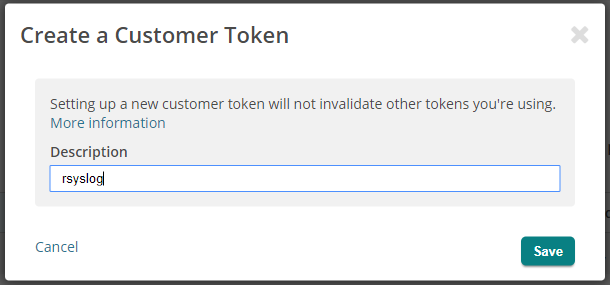
It is best to give this token a description.
Finally, you will have a token that you’ve got the option to use.
Copy this for use later in our configuration files.
Below is a default configuration file located in/etc/rsyslog.d/22-remote.confthat will tell rsyslog to sendsyslogevents to Loggly.
The number22is not important, this is merely a way to define the order of loading the configuration files.
Choose a number that makes sense in your configuration.

Theactionconfiguration is for sending allSyslogmessages to Loggly by default.
Finally for this configuration to take effect, we need to restartrsyslog.
Additionally, to turn on a higher level of logging, add the following lines to yourrsyslog.conffile and restartrsyslog.
Conclusion
The combination of rsyslog and Loggly is a powerful one.
Allowing you to consolidate, validate, and analyze your logs is important to maintaining a proper security posture.