Quick Links
GitLab CI’s Variables system lets you inject data into your CI job environments.
Variables are available within the job’s environment.
These include details of the commit, branch, and merge request that the pipeline’s running against.
The predefined variables also provide access to per-job credentials for accessing other GitLab features such as theContainer RegistryandDependency Proxy.
Beyond these built-in variables, you’ve got the option to set your own values in multiple places.
Similarly, for group-level variables, navigate to the group and use the sidebar to reach its CI controls.
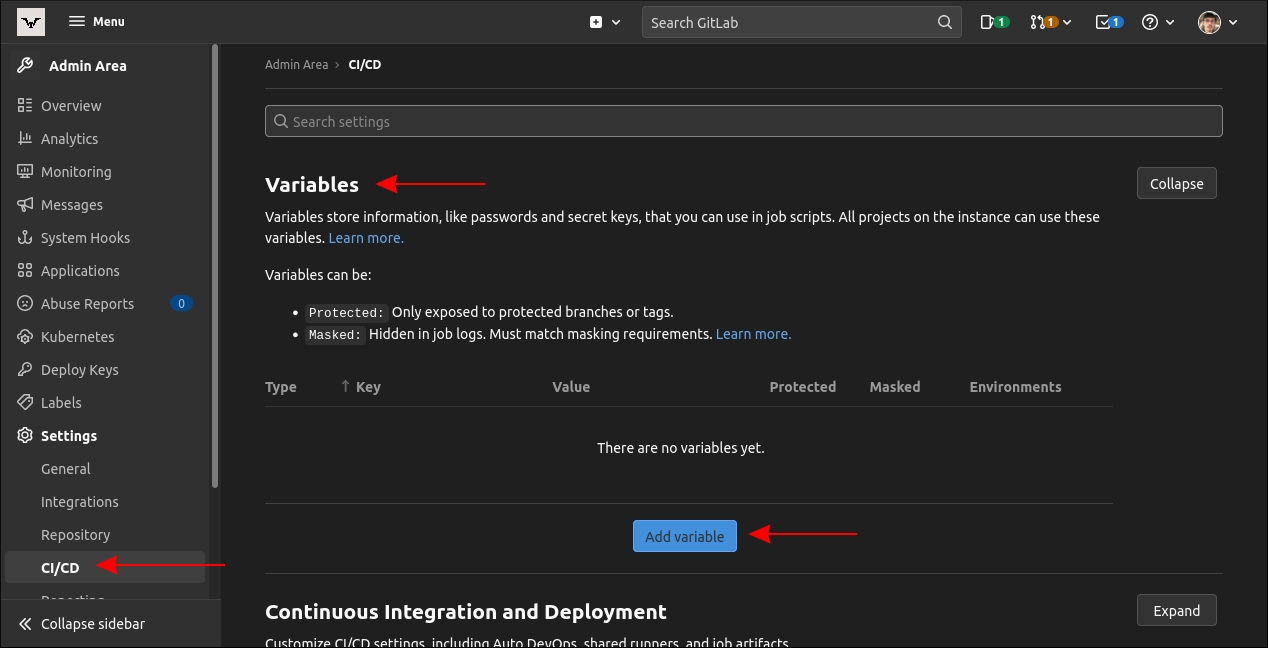
Instance-level variables are located via the same route in the GitLab Admin Area.
Expand the “Variables” section to view any variables that have already been defined.
tap the blue “Add variable” button to begin adding a new item to the list.
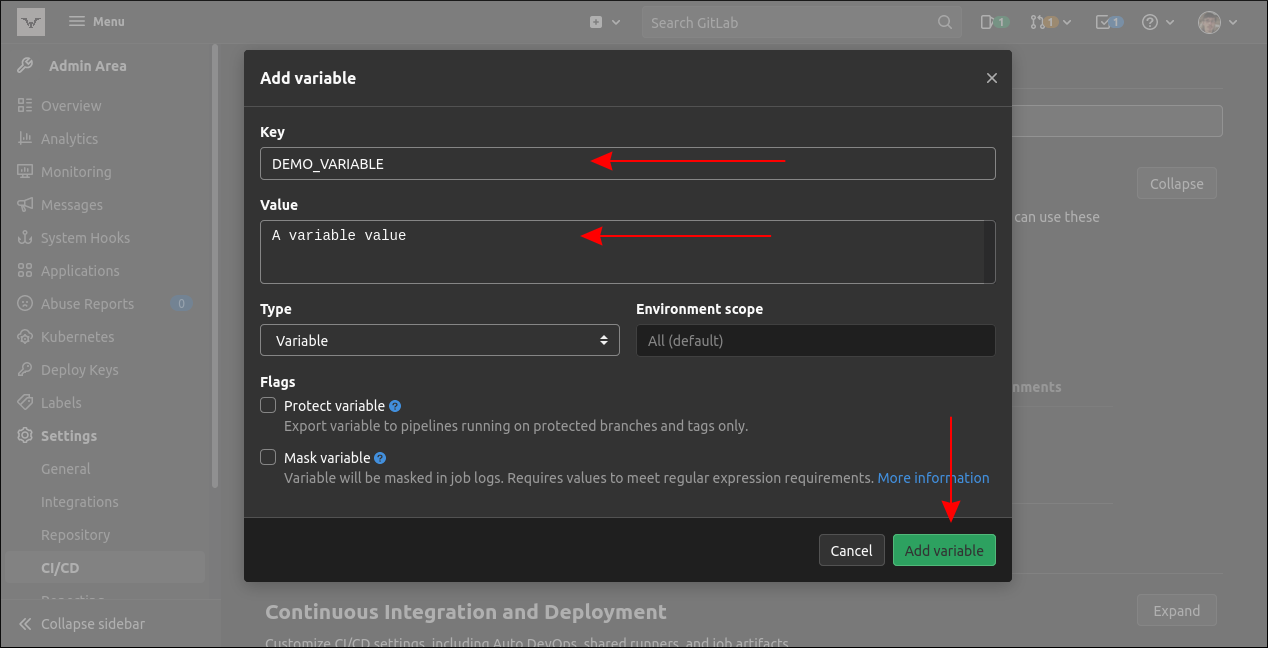
All variables should be a valid string containing only alphanumeric characters and underscores.
Next set the value of your variable.
Once you’re done, hit the green “Add variable” button to complete the process.
you could now reference your variable in pipelines that execute within the scope you defined it in.
This dialog also provides a way to delete redundant variables.
This option means the variable will only be defined in pipelines running against protected branches or tags.
When this checkbox is enabled, GitLab will automatically filter the variable’s value out of collected job logs.
Successful masking requires variable values to be reliably detectable within the logs.
Consequently it only works for values that meet specificformatting requirements.
Most common authentication token formats, as well as all Base64-encoded data, will be compatible.
Masking only works for values up to 4 KiB in size.
Environment-Level Variables
Variables can be assigned to specificenvironments.
This feature lets your pipelines operate with different configuration depending on the environment they’re deploying to.
The variable will only be defined in pipelines which reference the selected environment via theenvironmentfield in the.gitlab-ci.ymlfile.
Setting Variables In
.gitlab-ci.ymlVariables can be defined within your.gitlab-ci.ymlfile usingavariablesblock.
Variables can be set at the pipeline level with a globalvariablessection.
Individual jobs can have their own variables too.
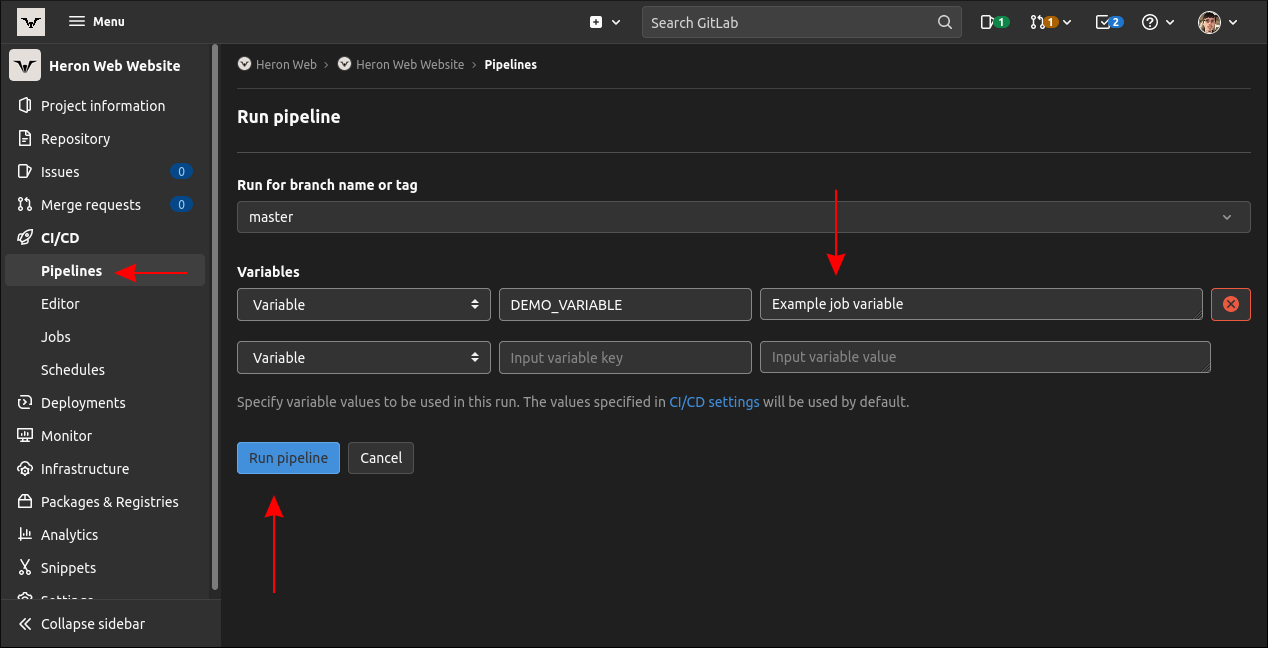
Use the dropdown menu to go for the branch or tag to spin up the pipeline against.
Next use the “Variables” table to define variables to add to this pipeline run.
These will become the most specific values, applied as the final stage in the variable precedence order.
Variables set here won’t be saved or reused with any future pipeline.
Summary
GitLab’s CI variables implementation is a powerful and flexible mechanism for configuring your pipelines.
you could always override a variable later in specific projects that need a different value.