Instead, you’ll likely need to delete its partitions and repair the Windows boot loader on your own.
If you installed Ubuntu or a similarLinux distributionlike Linux Mint with Wubi, it’s easy to uninstall.
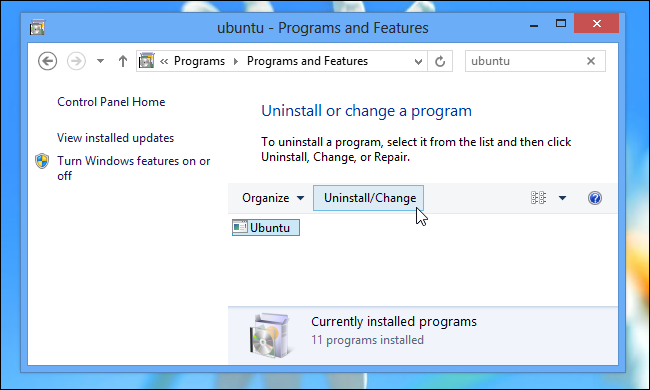
Just boot into Windows and head to Control Panel > Programs and Features.
Find Ubuntu in the list of installed programs, and then uninstall it like you would any other program.
The uninstaller automatically removes the Ubuntu files and boot loader entry from your gear.
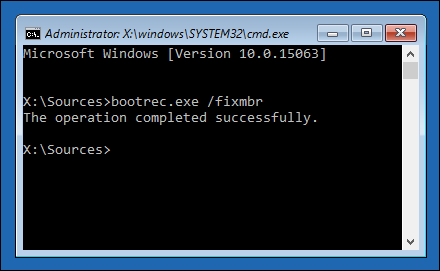
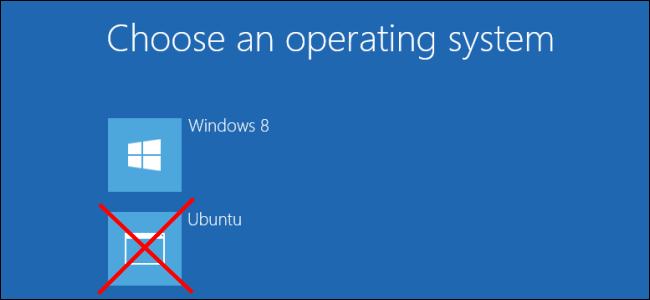
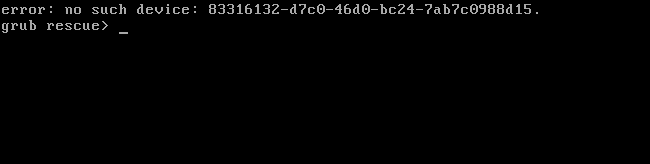
After deleting the partitions, the GRUB boot loader won’t boot your machine properly.
Let’s take a closer look at how to get all that done.
Start by booting into Windows.
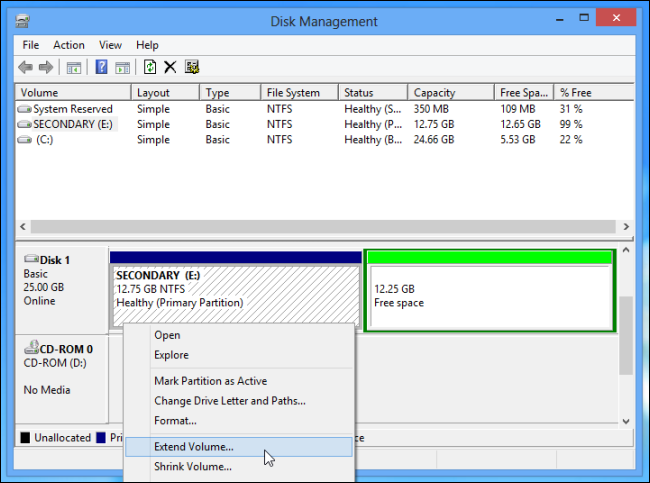
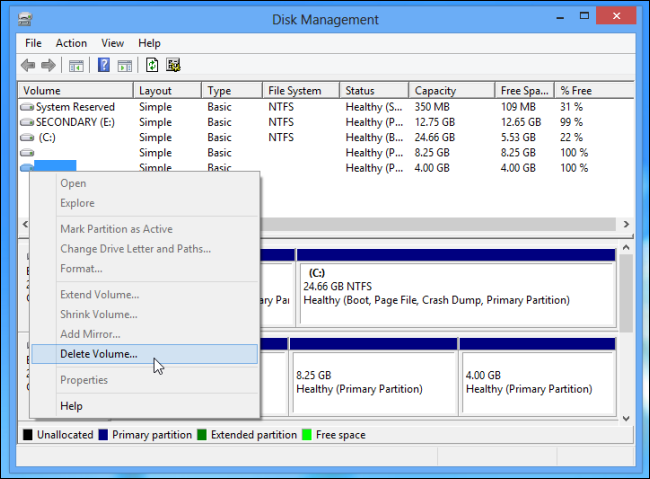
In the Disk Management app, locate the Linux partitions, right-click them, and delete them.
Extend the partition so that it takes up all of the available free space.
Any free space on your hard drive will remain unusable until you assign it to a partition.
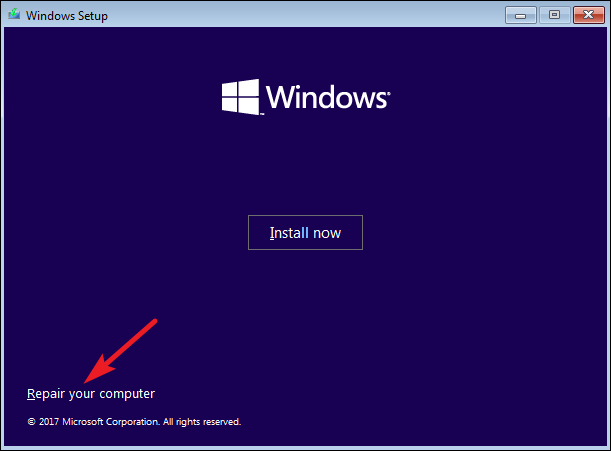
You’re going to be accessing the Command Prompt from the recovery environment.
We’re covering Windows 10 here, but the instructions will also work for Windows 8.
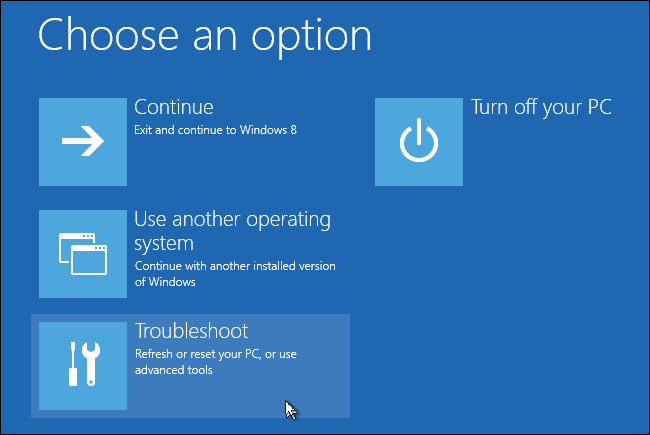
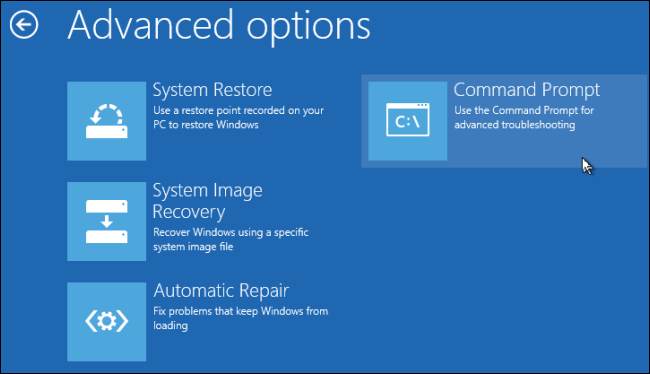
On the “Choose an option” screen, nudge the “Troubleshoot” option.
On the “Advanced options” screen, poke the “Command Prompt” option.
It will boot from its hard drive, starting Windows normally.
All traces of Linux should now be erased.