This command not only displays the output on screen but also records it in aseparate log file.
This command helps you to troubleshoot a process as it maintains a written record of processes.
What Is the tee Command on Linux?
The Linuxteecommand is a useful tool for saving time and improving efficiency on Linux.
Theteecommand works like a T-shaped pipe that splits water into two directions.
It lets you view the output of a program and save it in a file simultaneously.

Theteecommand does both things together.
It lets you copy the output to the files or variables you choose and display it to you.
This command is also used inshell scriptsand terminal commands to send output to different locations.
Hannah Stryker / How-To Geek
you could use theteecommand tomake backups, find errors in scripts, and keep track of system logs.
Theteecommand also lets youpipe it with other commands.
Almost all Linux distributions come with theteecommand pre-installed, which is part of the Coreutils package.

Theteecommand follows a similar syntax as other Linux commands.
-i or –ignore-interrupts
Ignore interrupt signals such as Ctrl+C.
–help
Display a basic help related to the command options.
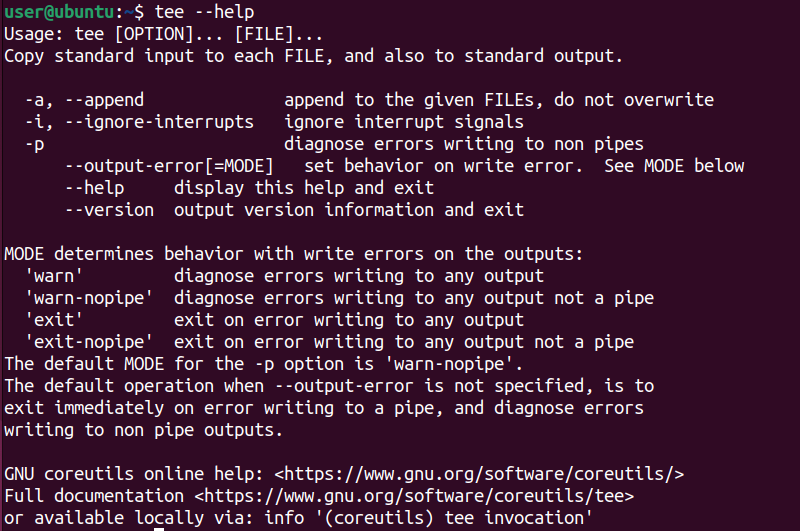
–version
Display theteecommand version.
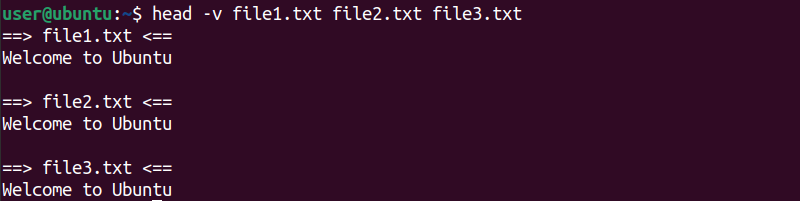
Lets perform another example with aechocommandto save and view the output.
First, use theechocommand to print text on the terminal.
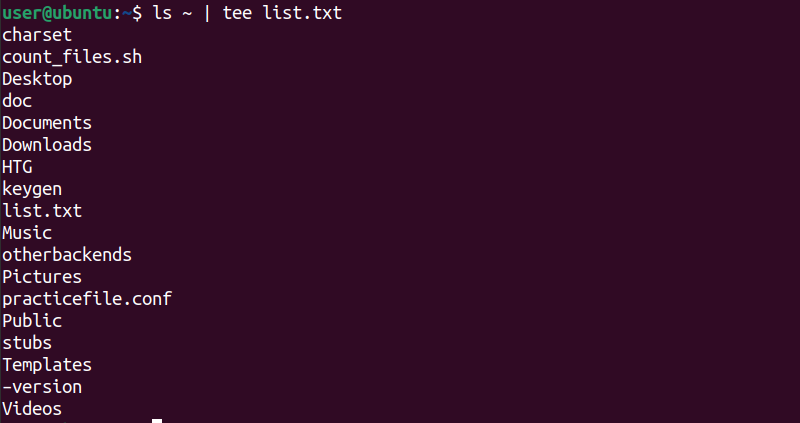
After that, piped theteecommand with theechocommand to write the same text to a file called “output.txt”.
Finally, use thecatcommandto verify the contents of the “output.txt” file.
You just have to define the file names after theteecommand that you want to write to.
Simply separate them with spaces.
It also displays them on the terminal.
Just throw in the file names after theteecommand with spaces between them.

Append Output to a File Using tee
Theteecommand on Linux overwrites the file content by default.
In such cases, you have to direct the command output to the/dev/nulldevice.
The/dev/nullis often referred to as a “null unit” or “null file.”

Consider the following example:
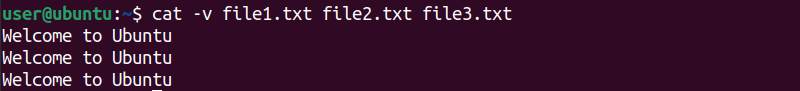
Theechocommand output “Welcome to Ubuntu” is written to the output.txt file.
After that, the pipeline operator is used with theteecommand.
This will pass the file content to thewccommand.

Thewccommand will output the total characters counted and display an integer value.
However, some files and directories such as system directories or protected files require superuser privileges to modify.
To write to these files or files owned by other users, useteein conjunction withsudo.
However, when you use thesudowith theteecommand, this will run without any error.
you could use thesudocommand to run theteecommand as the root user or the owner of the file.
Simply prependsudowith theteecommand:
First, theteecommand will take theechocommand output.
After that, it elevates tosudopermissions and writes the text to the file.
Examples of Using tee in a Bash Script
Theteecommand can be useful in various scripting scenarios.
It helps you to log or capture the output of a command for further processing or debugging.

Theteecommand will not only display output but also save it to a file or files for later use.
Theteecommand writes this output to the terminal and the file log.txt.
If the file log.txt does not exist, it will be created.

If it exists, it will be overwritten, unless you use the-aoption to append to the file.
This script prints the date and time to the terminal and to two files named log1.txt and log2.txt.
Read both files content usingcatcommand.

Lets consider another simple bash script that takes an input and stores it inside a log fileusing theteecommand.
Then, use theechocommand and thereadcommand to prompt you to enter some text and store it in a variable.
Finally, use theechocommand again to give feedback.

This will tell you that your input has been logged into the file.
initiate the bash script usingbashcommand.
This includes CPU and memory usage, disk I/O, and web link activity.

Identifying performance bottlenecks helps optimize system resources and ensures that your system operates efficiently.
Like theteecommand, Linux hasmultiple other commandsthat help you monitor the processes easily.
Some of the main commands includeps,top, andpgrepcommand.

Linux’s systems often run multiple processes simultaneously.








