Quick Links
Computer virus: Those two words instantly make us sweat—and for good reason.
Since the 1980s, viruses have wreaked havoc on everything fromour inboxestoindustrial facilities.
To remedy the situation, you’re instructed to call brothers Basit and Amjad Farooq Alvi.

solarseven/Shutterstock.com
The virus was known asBrain, the first PC virus.
It was technically built for the protection of software.
However, the good intentions didn’t last.

Audrius Merfeldas/Shutterstock.com
Millions of viruses have existed since Brain in 1986.
However, some have been considerably worse than others.
Melissa - 1999
In 1999,computer viruseswere still a relatively new concept.

Tero Vesalainen/Shutterstock.com
While that may not seem like that big of a deal, it was.
According tothe FBI, many corporate and government email servers became overloaded and had to be shut down.
In addition, internet traffic slowed to a trickle.
Nicescene/Shutterstock.com
This virus did have a happy ending.
ILOVEYOU - 2000
Who doesn’t want to find a love letter in their inbox?
TheILOVEYOUvirus (known as Love Bug back then) wastechnically a wormand started as a seemingly innocent email.
The subject line, “ILOVEYOU,” drew email users to click.
Inside, a text file titled “LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU.TXT.VBS” was waiting.
Even worse, it would attach itself to all the addresses in Microsoft Outlook, spreading like wildfire.
As a worm, no further human intervention was required to keep ILOVEYOU moving.
As a result, millions of computers became infected in only a matter of days.
In fact, it’s regarded by many as the first severe attack on a corporate system.
The Code Red worm specifically targeted systems running Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) for Windows Server.
Important websites would display “Welcome to http://www.worm.com!
Hacked by Chinese!”
The worm was also the cause of various dangerousdenial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
But that ominous-sounding name?
It was inspired by the drinkthe security employeeswere sipping when they found the worm: Mountain Dew Code Red.
As a worm, Nimda was similar to ILOVEYOU and Code Red in that it replicated itself.
Nimda affectedWindows operating systemsand was able to modify system files and even create guest accounts.
The actual cost of Nimda has yet to be fully estimated.
But trust us when we say it’s a lot.
Opening weird attachments from email addresses you don’t recognize is a big no-no.
And while many email users today know this, things were different in 2003.
The Sobig worm infected millions of Microsoft computers via email.
And inside, there would be an attachment just begging for a click.
Due to its spreading capabilities, Sobig overwhelmed networks worldwide and resulted in billions of dollars in damages.
Mydoom - 2004
“I’m just doing my job, nothing personal, sorry.”
This was the email message sent by the email worm, Mydoom, first discovered in 2004.
And a job it did, indeed.Mydoomquickly became the fastest-growing email worm in history.
In fact, it still holds the title.
Similar to Sobig and other worms on this list, Mydoom was primarily spread through email attachments.
The fast growth of Mydoom slowed internet traffic worldwide.
Mydoom was also behind multiple DoS andDDoS attacks, includingattacksagainst the US and South Korea.
Zeus - 2007
Zeus, also known as Zbot, is trojanmalware infecting Microsoft Windows.
The malware most commonly targets financial or banking information.
As a result, an attacker can control multiple computers at once.
Why is Zeus so dangerous?
For example, the malware can use keylogging to capture sensitive information such as online banking passwords.
Stuxnet - 2010
Stuxnetmade headlines in 2010 as the first worm developed to target industrial control systems.
The worm inflicted physical damage on Iran’s nuclear facilities, particularly centrifuges.
By exploiting vulnerabilities found within Windows to gain access to the software used to control the industrial equipment.
Stuxnet was also unique in that the worm was first introduced to computers using infected USB drives.
Yes, physicalUSB drives.
Even now, Stuxnet is hailed as the world’s first cyberweapon.
PoisonIvy - 2011
PoisonIvy does more than make its victims itch.
PoisonIvy was first identified in 2005.
However, one of the most notable attacks using the trojan occurred in 2011.
PoisonIvy is dangerous because threat actors can access a computer forkeylogging, screen capturing, and more.
The trojan is also used to steal passwords and other critical personal information.
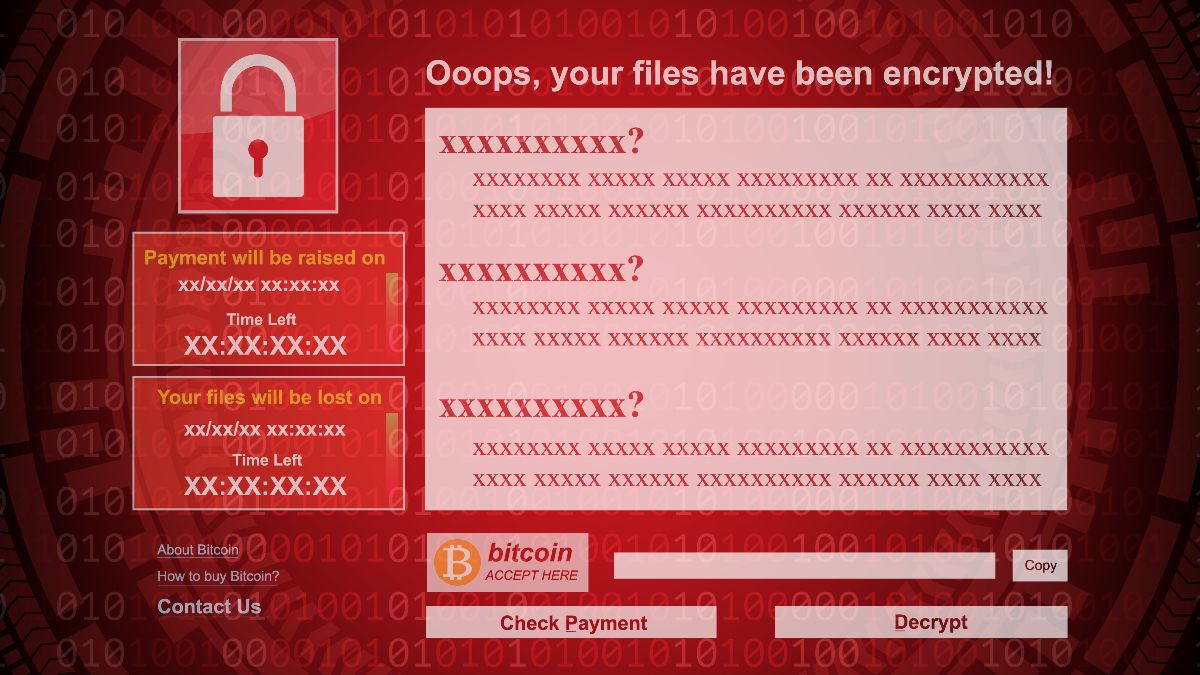
WannaCry - 2017
TheWannaCry ransomware attacktook place in May 2017.
The goal was simple: to hold a user’s files hostage and get paid inBitcoin.
The WannaCry attack used a leaked hack known asEternalBlueto gain access to computers running Microsoft Windows.
Once in, WannaCry would encrypt the computer’s data.
Then, users would see a message demanding a Bitcoin payment for the release of their files.
In 2017, the damagewas estimatedto be in the billions.
Even today, WannaCry still exists, highlighting the importance ofprotecting ourselves from ransomware.
The Computer Virus Is Alive and Well
As technology evolves, so does the work of cybercriminals.
Serious threats such asransomwareare alive and well.
The best thing you could do?Protect yourself.
Even the most basic security practices can help prevent viruses from infecting your devices.