Summary
There’s nothing wrong with traditional thermal compounds.
They’re cheap, reliable, and can keep your machine parts decently cool.
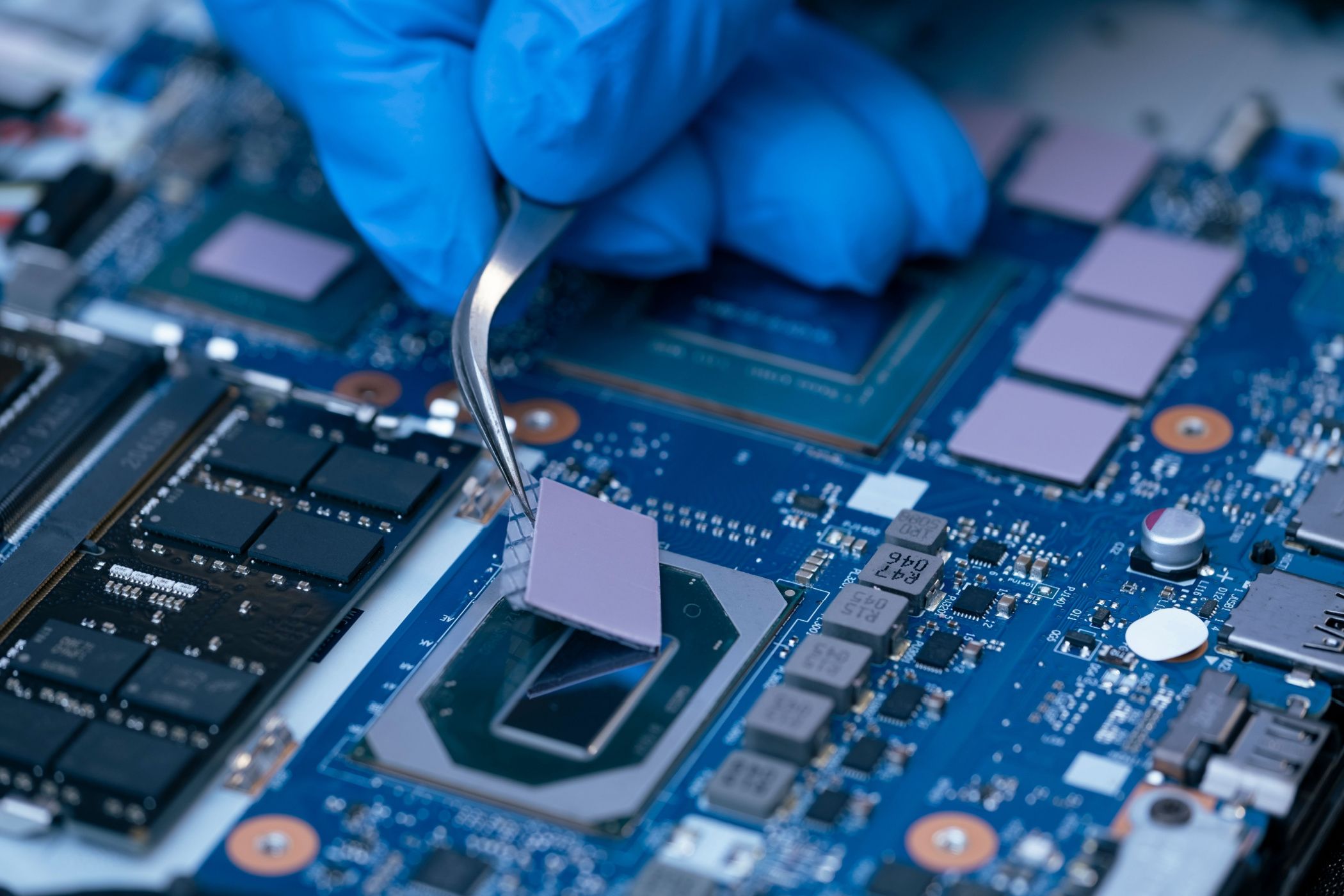
What Are Graphene Thermal Pads?
9Robot/Shutterstock.com
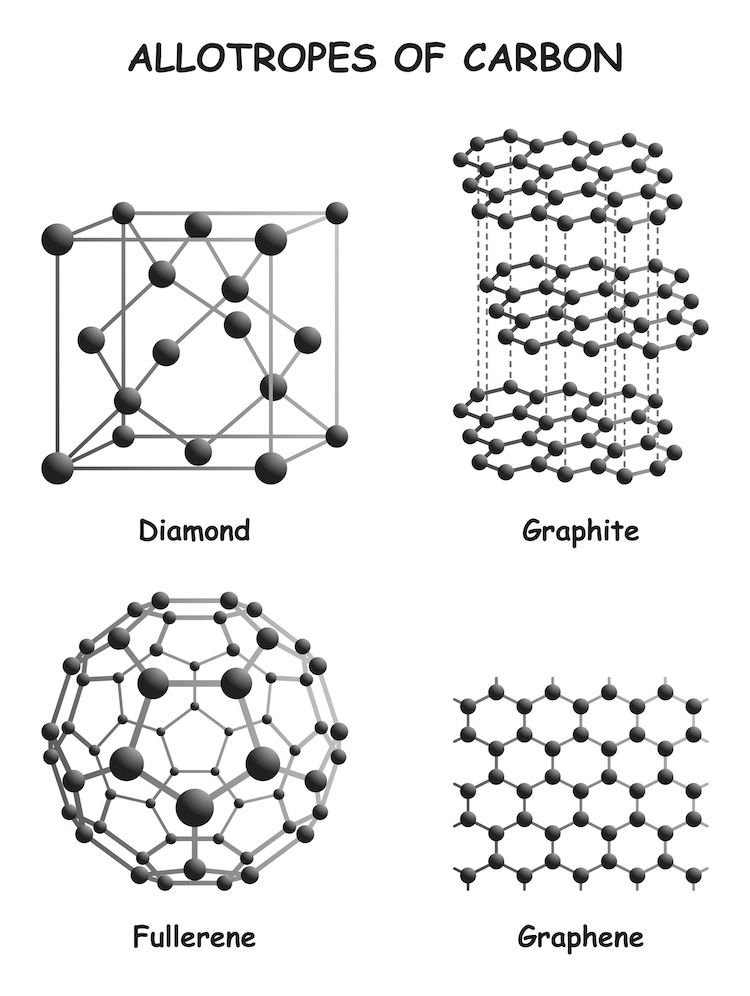
Graphene thermal pads are made ofgraphene, which is anallotrope of carbon.
What makes graphene pads so exciting is their excellent thermal conductivity.
Even so, it’s higher than a traditional non-metallic thermal paste’s thermal conductivity of about410W/mK.

Thermal Grizzly
In fact, graphene has potentiallyunlimited thermal conductivity, as its conductivity scales with size.
As the technology develops, we might see pads that outperform liquid metal a few years from now.
Graphene Thermal Pads vs.
udaix / Shutterstock.com
However, easier than liquid metal doesn’t exactly mean easy.
It doesn’t help the fact that graphene pads are incredibly delicate and hard to handle.
If you order a KryoSheet, check that you have a clean set of precision tweezers!
By exposing each layer of graphene directly to the surface, we get an exceptional thermally- and electrically-conductive material.
In a graphite pad, heat has to transfer between each layer of graphene until it reaches a heatsink.
But with a graphene pad, heat provides a direct pathway for heat to travel efficiently along its structure.
In theory, graphene thermal pads have vastly superior performance compared to graphite pads.
Another exciting alternative isphase-change thermal pads, which melt when they come into contact with a hot computer chip.