These parts are called “heatsinks.”
Without them, our computers would be significantly less powerful.
What exactly is a heatsink, though, and how does it work?
Kusalodom/Shutterstock
What Is a Heatsink?
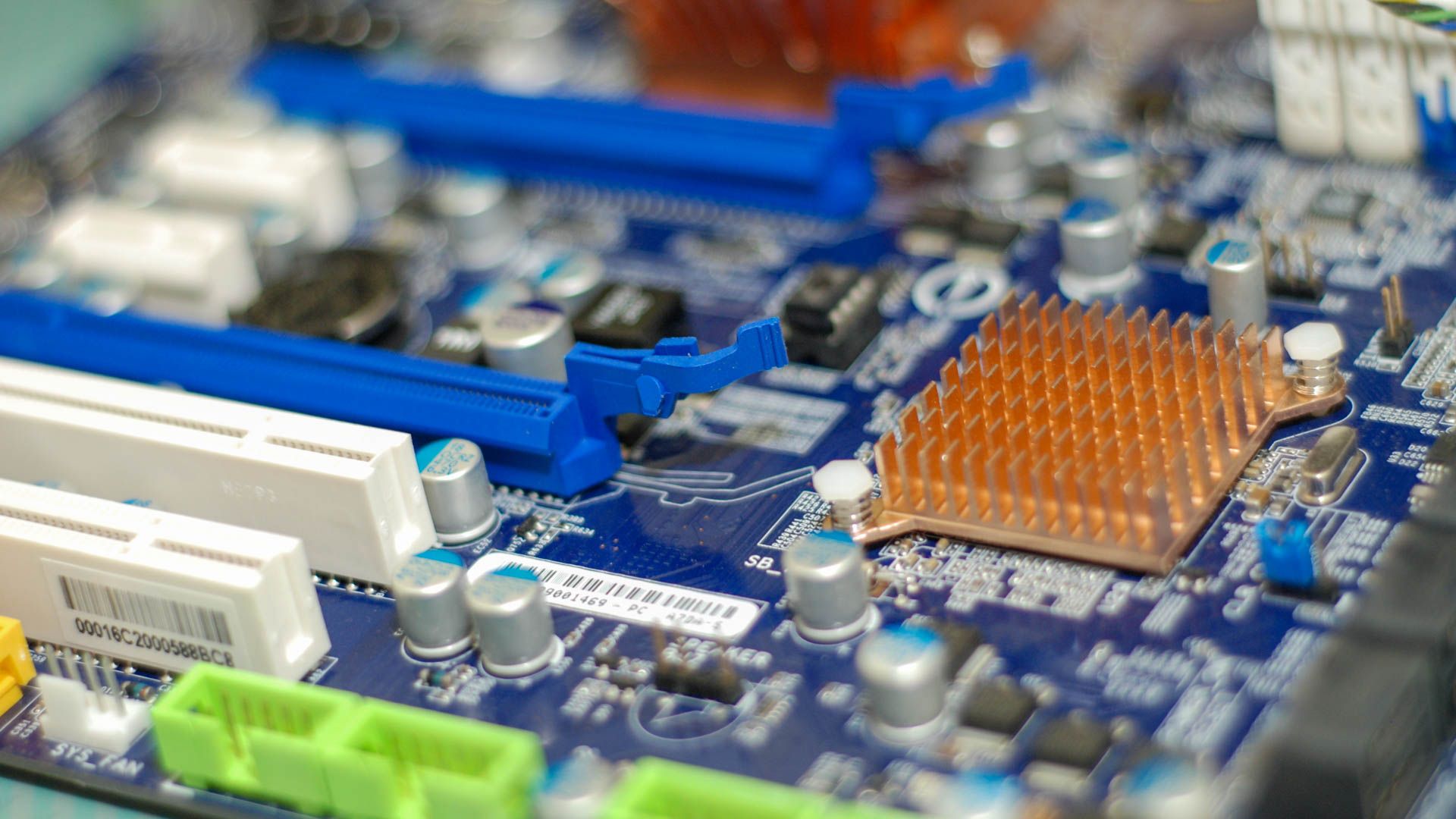
You will find heatsinks on all important components like yourCPU,graphics card, and some parts of themotherboard.
Budget RAM modules often omit heatsinks and pass the savings on to you.
Jason Fitzpatrick / How-To Geek
Heatsinks are essential for CPUs, graphics cards, and motherboards.
Without heatsinks, your box wouldn’t work correctly.
Many motherboards also have heatsinks on theVoltage Regulator Modules(VRMs) and M.2 NVMe.

Grigvovan / Shutterstock.com
As for graphics cards, they house a GPU, VRAM (memory), and VRMs.
These components are collectively covered under a single heatsink, often accompanied by one or more fans.
Heatsinks significantly improve the lifespan, performance, and stability of the components they sit on.
teh_z1b / Shutterstock
Types of Heatsinks
Heatsinks come in all kinds of shapes, sizes, materials, and designs.
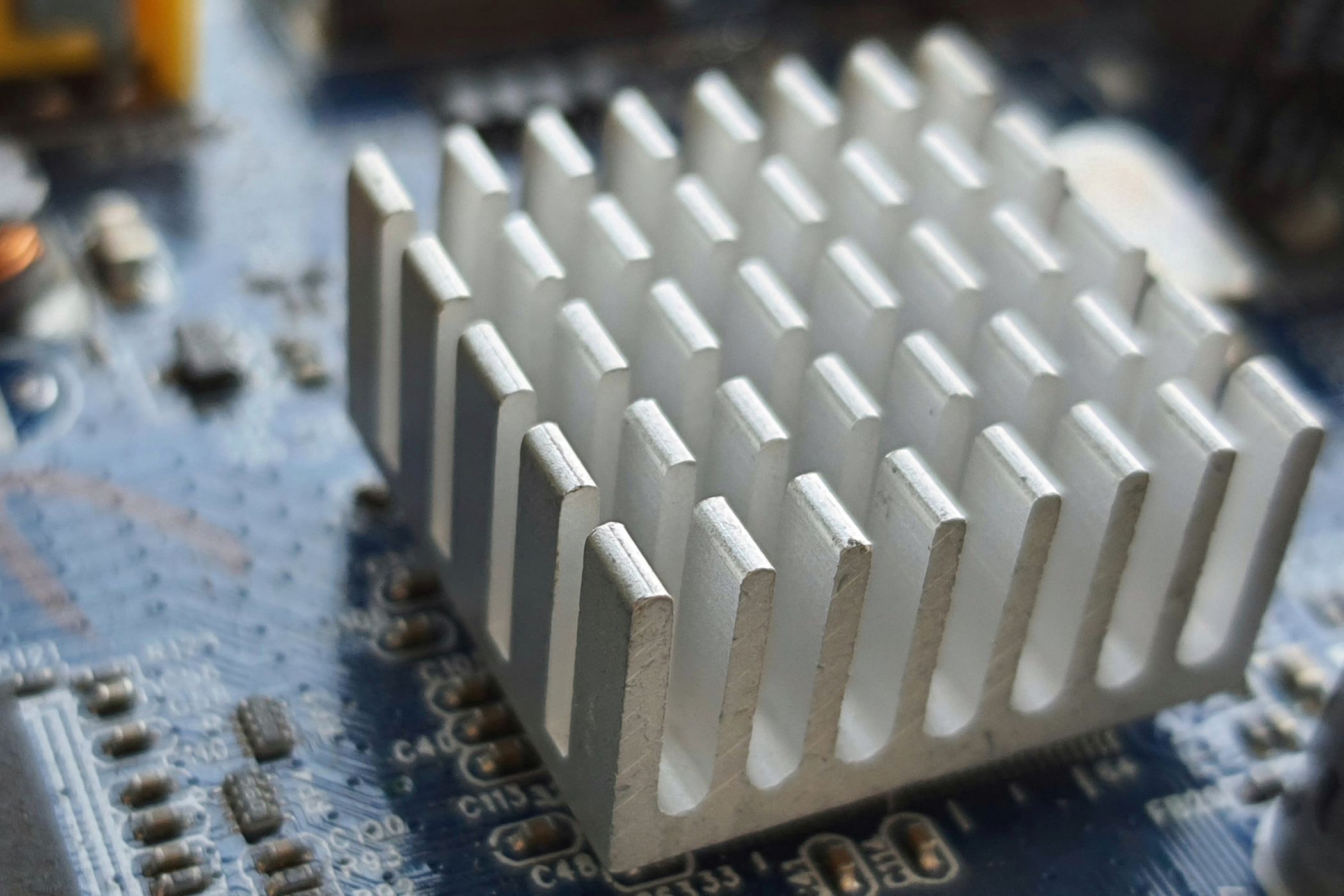
The most basic heatsinks are flat, relatively thin pieces of metal.
However, the most common jot down isfin heatsinks, which have thin ridges that resemble rows.
Ismar Hrnjicevic / How-To Geek
This throw in of design increases the surface area of the heatsink, which significantly improves its heat dissipation.
You’ll find fin heatsinks on your CPU, graphics card, and parts of the motherboard.
The heatsink releases the heat to the surrounding air, either passively or with the help of a fan.
All of these processes happen simultaneously.
However, some intricacies are involved in how exactly heatsinks operate.
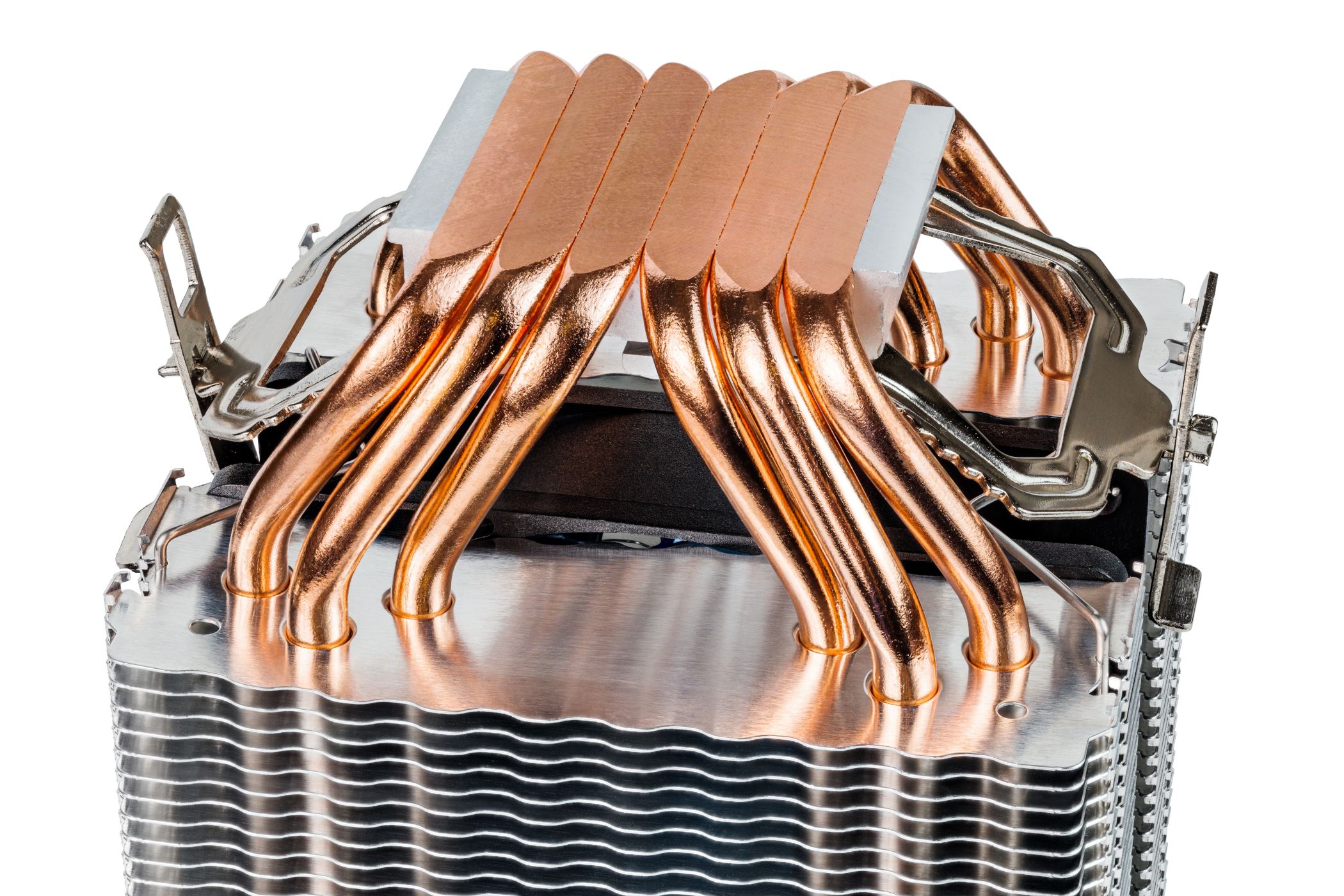
To better illustrate how heatsinks work, let’s use the example of a typical aftermarket air CPU cooler.
We call this part of the cooler the base plate.
Heat pipes are typically made of copper or aluminum with some bang out of liquid inside of them.
Heat pipes are in direct contact with the heatsink fins, and the heat slowly transfers over to them.
As this is happening, the vapor inside the heat pipe condenses and turns back into a liquid.
The liquid is once again ready to repeat the cycle.
Instead, the heat slowly transfers from the thick base plate onto the fins.
Factors That Affect Heatsink Effectiveness
Several factors can influence the efficiency of a heatsink.
They’re far from the only method of cooling PC parts, though.