What is LVM?
Logical Volume Manager allows for a layer of abstraction between your operating system and the disks/partitions it uses.
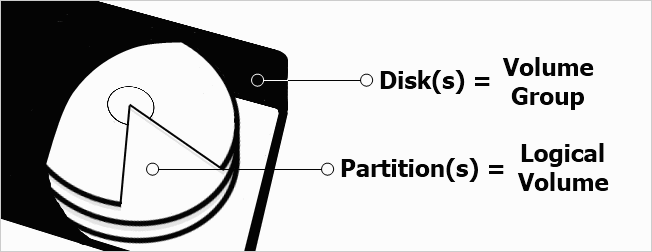
and then looks at what partitions are available on those disks (/dev/sda1, /dev/sda2, etc.).
With LVM, disks and partitions can be abstracted to contain multiple disks and partitions into one unit.
In addition, LVM can give you features that your file system is not capable of doing.
When Should You Use LVM?
Some distributions, like Fedora, install with LVM by default.
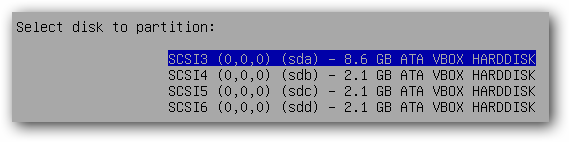
To install Ubuntu using LVM it’s crucial that you use the alternate install CD.
Download it from the link below and burn a CD oruse unetbootin to create a USB drive.

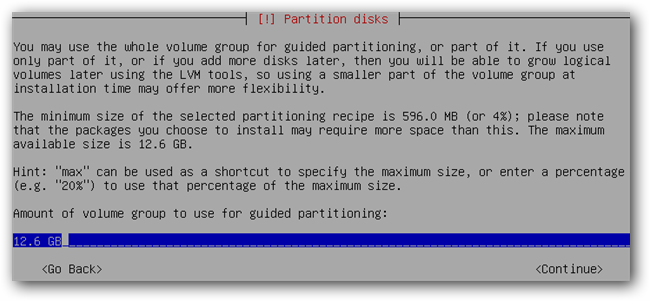
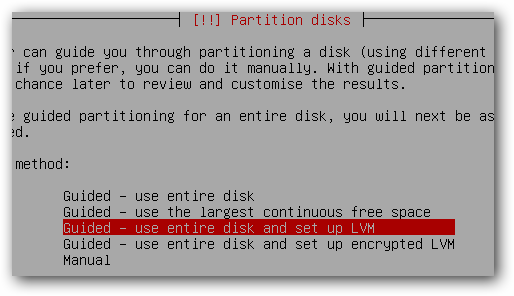
pick the size you want the first logical volume to be and then continue.
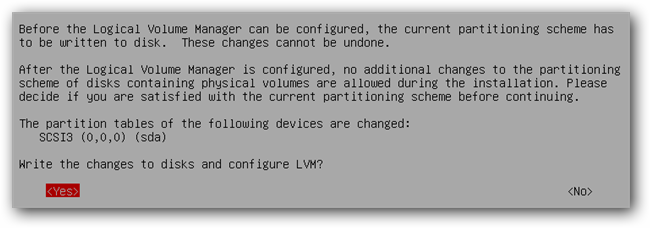
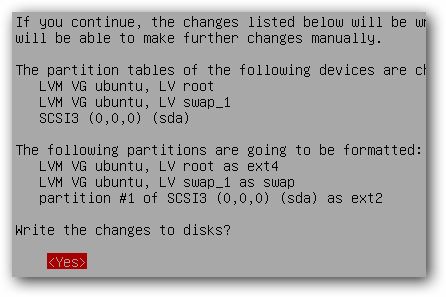
Confirm your disk partitions and continue with the installation.
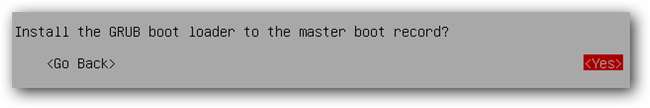
The final step will write the GRUB bootloader to the hard drive.
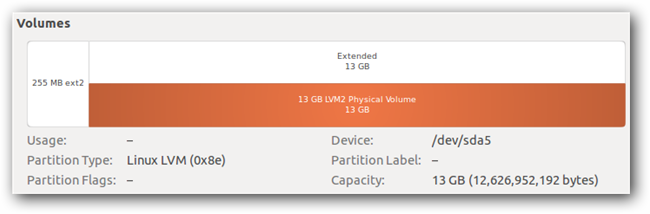
Ubuntu will automatically create a 255 MB ext2 partition for your bootloader.
After the installation is complete, reboot the machine and boot into Ubuntu as normal.
There should be no perceivable difference between using LVM or traditional disk management with this punch in of installation.
To use LVM to its full potential, stay tuned for our upcoming article on managing your LVM installation.