These options don’t need to be overwhelming.
If you’re not sure which Linux file system to use, there’s a simple answer.
Ext4 is the default file system on most Linux distributions for a reason.
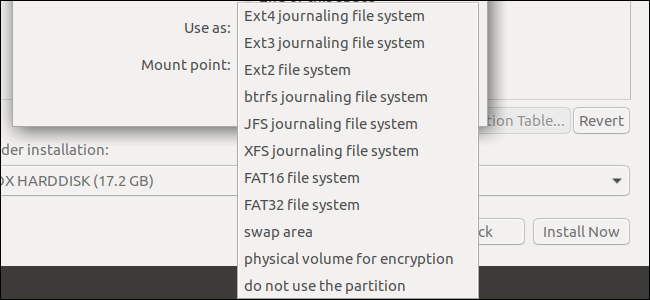
It’s an improved version of the older Ext3 file system.
In the future, Linux distributions will gradually shift towards BtrFS.
The risk of data corruption or other problems isn’t worth the potential improvement in speed.
Related:FAT32 vs. exFAT vs. NTFS: What’s the Difference?
You’ll want touse exFAT or FAT32when formatting an external drive on Linux.
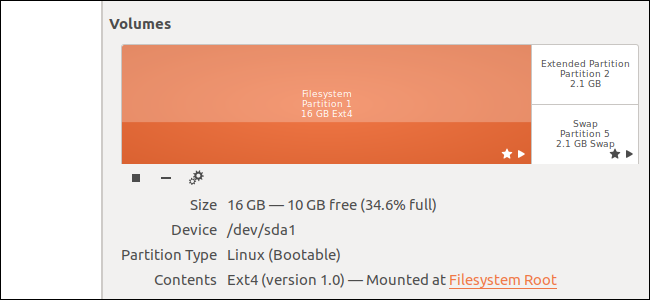
This partition is used for “swap space”.
It’s similar to the paging file on Windows.
Linux swaps out memory to the swap space when its RAM is full.
This partition must be formatted as “swap” instead of with a particular file system.

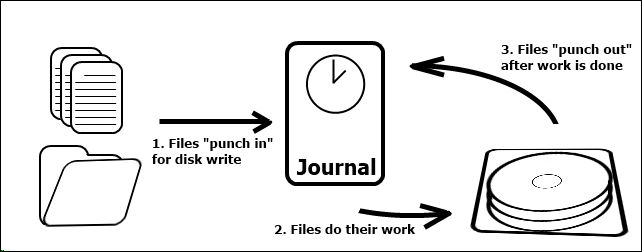
What Is Journaling?
Journaling is designed to prevent data corruption from crashes and sudden power loss.
Let’s say your system is partway through writing a file to the disk and it suddenly loses power.

Without a journal, your machine would have no idea if the file was completely written to disk.
The file would remain there on disk, corrupt.
This prevents data loss and file corruption.

It’s not as much overhead as you might think.
The full file isn’t written to the journal.
What’s the Difference Between All Those Linux File Systems?
While Microsoft develops Windows and Apple controls macOS, Linux is an open-source project developed by the community.
Anyone (or any company) with the skill and time can create a new Linux file system.
That’s one reason why there are so many options.
But these are the options you’ll most frequently see when using Linux.
Linux Commands
Files
tarpvcattacchmodgrepdiffsedarmanpushdpopdfscktestdiskseqfdpandoccd$PATHawkjoinjqfolduniqjournalctltailstatlsfstabecholesschgrpchownrevlookstringstyperenamezipunzipmountumountinstallfdiskmkfsrmrmdirrsyncdfgpgvinanomkdirdulnpatchconvertrcloneshredsrmscpgzipchattrcutfindumaskwctr
Processes
aliasscreentopnicereniceprogressstracesystemdtmuxchshhistoryatbatchfreewhichdmesgchfnusermodpschrootxargsttypinkylsofvmstattimeoutwallyeskillsleepsudosutimegroupaddusermodgroupslshwshutdownreboothaltpoweroffpasswdlscpucrontabdatebgfgpidofnohuppmap
Networking
netstatpingtracerouteipsswhoisfail2banbmondigfingernmapftpcurlwgetwhowhoamiwiptablesssh-keygenufwarpingfirewalld