Summary
Frustrated because your trusty old laptop overheats or even shuts down all the time?
Perhaps you don’t have to replace it just yet.
One cheap way to fix the issue is by replacing the thermal paste.

R. Rizvanov/Shutterstock.com
What Is Thermal Paste?
The heat from your processor transfers into the heat sink, which in turngets cooled off by a fan.
This makes it possible for tiny pockets of heat-insulating air to get trapped between them.
Thermal paste fills in those gaps and makes it easier for heat to move across the interface.
Without thermal paste, the processor wouldn’t be able to dissipate enough heat.
Your laptop could overheat and shut down or slow down its performance.
What’s worse is that you’d risk permanently damaging your processor.
Your laptop already has thermal paste inside of it.
The laptop manufacturer applied it and tested your machine before shipping it off.
How Often Does My Laptop’s Thermal Paste Need Replacing?
We call this processthermal throttling.
Because your laptop has to constantly endure high temperatures, the thermal paste dries out over time.
Nevertheless, you’ll see a considerable difference if you keep your laptop dust and pet fur free.
Use a can of compressed air once or twice a month to quicklyclean the inside of your laptop.
Replacing the thermal paste might have a nice bonus side effect ofmaking your laptop run faster.
Tearing down your laptop to replace the thermal paste can be a risky procedure.
It has many delicate parts, such as ribbon cables, a circuit board, and a battery.
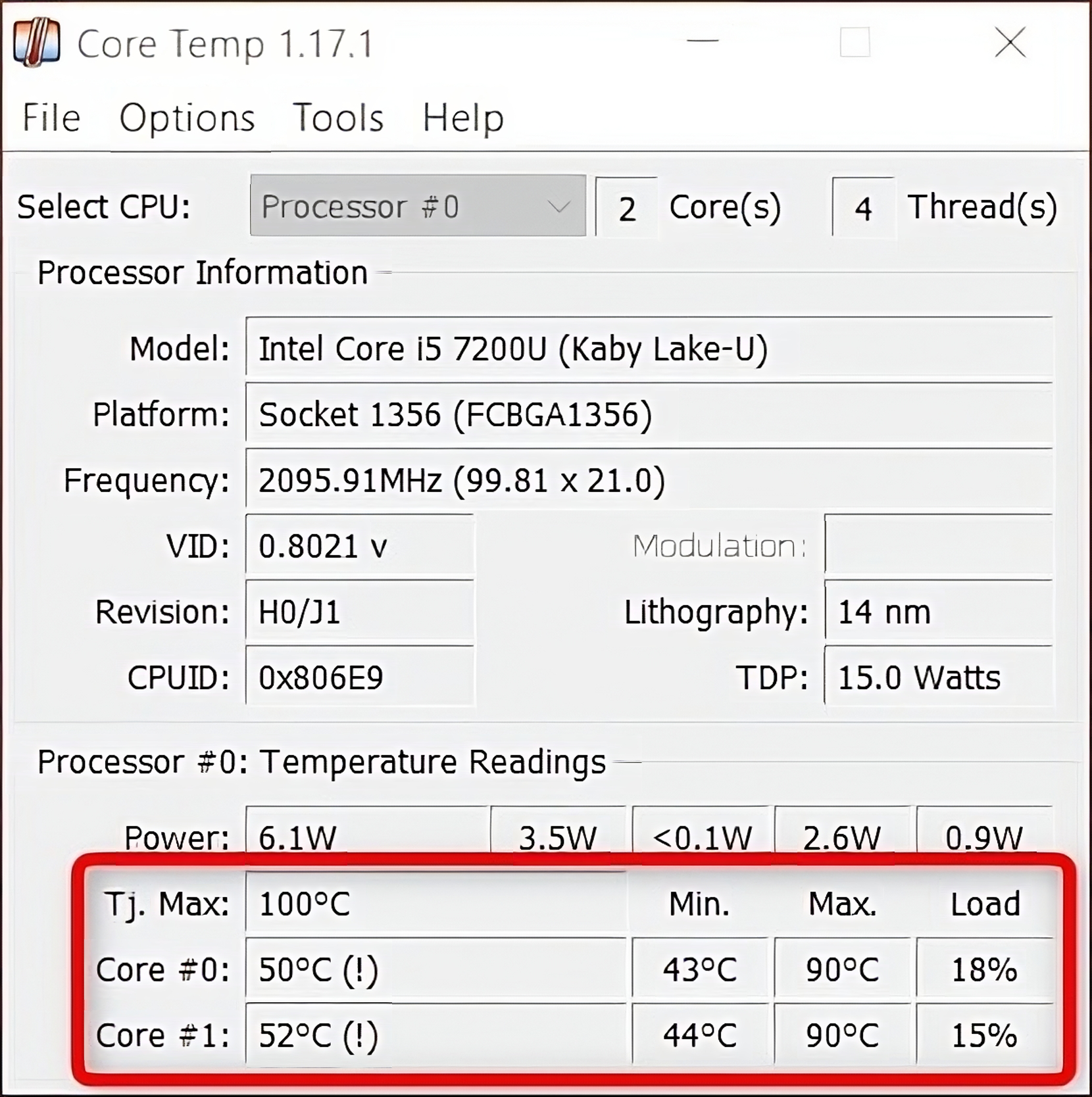
The easiest way to check your CPU’s temperature is by installing afree temperature monitoring program.
We recommendCore Tempfor basic monitoring orHWMonitor, which can also check GPU temps.
After installing Core Temp, you might see the Tj.
Max (the maximum safe operating temperature), current, minimum, and maximum temperatures for each core.
Launch a video game, video editor, or even an internet online window with many tabs open.
After using the laptop for about 15 minutes, check the current temperature on Core Temp.
While the “normal” temperatures vary based on your CPU model, sustained temps near the Tj.